Introduction

The periodic table of elements is a fundamental tool used to understand the chemical reactions and properties of various substances. Understanding the charges of these elements is crucial for predicting their behavior in chemical reactions. This article provides a printable periodic table of elements with their charges, along with an in-depth explanation of their significance and applications. Additionally, common mistakes to avoid and a step-by-step approach to using the table are covered.
Charge of Elements
The charge of an element refers to the electrical charge carried by its atoms. It is determined by the number of protons and electrons present in the atom. Protons have a positive charge, while electrons have a negative charge. The charge of an atom is typically represented as a superscript after the element’s symbol. For example, sodium (Na) carries a charge of +1, indicating that it has one more proton than electron.
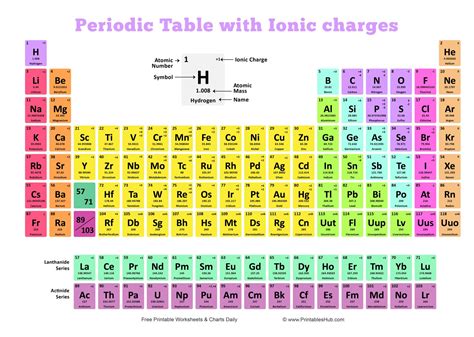
Periodic Table with Charges
The printable periodic table of elements with charges provided in this article allows for easy reference of the charges of different elements. It is organized in a way that highlights the trends in charges across the periodic table.
Significance of Charges
The charges of elements play a significant role in their chemical properties and reactivity. Some of the crucial implications include:
- Ionic Bond Formation: Elements with opposite charges attract each other and form ionic bonds. For example, sodium (Na+) and chlorine (Cl-) form sodium chloride (NaCl) through an ionic bond.
- Solubility: The charges of ions affect their solubility in different solvents. For example, sodium chloride is highly soluble in water, while calcium sulfate (CaSO4) is sparingly soluble due to the charges of its ions.
- Acid-Base Reactions: The charges of elements help determine the acidic or basic nature of their oxides. For example, sodium oxide (Na2O) is a basic oxide, while sulfur trioxide (SO3) is an acidic oxide.
- Redox Reactions: Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between elements, which changes their charges. Understanding the charges of the elements involved is essential for predicting the products and balancing these reactions.
Applications
The knowledge of element charges has numerous applications in various fields:
- Electrochemistry: Charge plays a crucial role in electrochemical reactions, such as battery operation, electroplating, and corrosion.
- Inorganic Chemistry: Understanding charges is fundamental to comprehending the structure and properties of inorganic compounds.
- Materials Science: Charges influence the electrical and magnetic properties of materials, which is important for developing advanced materials for electronics and energy storage.
- Biochemistry: The charges of ions are critical for understanding biological processes, such as nerve impulses and muscle contraction.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these common mistakes when working with the periodic table of charges:
- Assuming the Charge: Do not assume the charge of an element based on its position in the periodic table. Refer to the table or a reference source for the specific charge.
- Confusing Groups: The periodic table groups elements with similar chemical properties, but charges may vary within a group. Always check the charges.
Step-by-Step Approach
Follow these steps to effectively utilize the periodic table of charges:
- Identify the Element: Locate the desired element on the periodic table.
- Check the Charge: Observe the superscript associated with the element’s symbol to determine its charge.
- Apply to Chemical Reactions: Consider the charges of elements when predicting chemical reactions and understanding compound properties.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Why do some elements have multiple charges?
– Some elements have multiple charges due to their ability to lose or gain electrons in different chemical environments. -
How can I determine the charge of an ion?
– The charge of an ion is typically determined by the difference in protons and electrons in the atom. For example, an anion is formed when an element gains electrons, resulting in a negative charge. -
What is the most electronegative element?
– Fluorine (F) is the most electronegative element, meaning it has the highest tendency to attract electrons. -
What is the relationship between charges and chemical bonding?
– Charges play a crucial role in chemical bonding. Elements with opposite charges tend to form ionic bonds, while elements with similar charges form covalent bonds. -
How does the charge of an ion affect its solubility?
– The charge of an ion influences its solubility in different solvents. Generally, ions with similar charges tend to have lower solubility in polar solvents. -
What are the applications of the periodic table of charges in biochemistry?
– The periodic table of charges is used in biochemistry to understand the role of ions in biological processes, such as nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction. -
How can I use the periodic table of charges to balance redox reactions?
– Balancing redox reactions requires understanding the charges of the elements involved. By considering the changes in charges, it becomes easier to equate the number of electrons lost and gained. -
What is the impact of charge on the electrical properties of materials?
– The charge of ions affects the electrical properties of materials. For example, materials with ions that carry high charges tend to exhibit higher electrical conductivity.
Conclusion
The periodic table of elements with charges is a valuable tool for predicting chemical reactions and understanding substance properties. By referring to this table, chemists and scientists can gain insights into the behavior of elements in different chemical environments. The applications of the periodic table of charges extend to a wide range of fields, including electrochemistry, inorganic chemistry, materials science, and biochemistry. By avoiding common mistakes and following a step-by-step approach, individuals can effectively utilize this table to enhance their understanding of elemental chemistry.
Additional Resources
- Interactive Periodic Table of Elements with Charges
- Periodic Table with Charges and Ionization Energies
- Periodic Chart with Charges and Electron Configurations
Keywords
- Periodic Table
- Element Charges
- Ionic Bond Formation
- Acid-Base Reactions
- Redox Reactions
- Electrochemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Science
- Biochemistry