Introduction
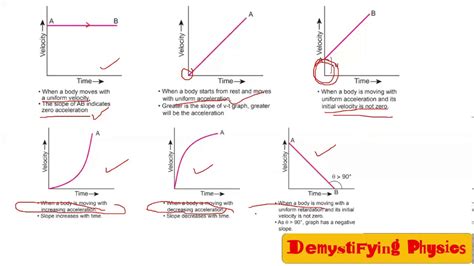
In physics, velocity is a measure of how quickly an object is moving and its direction. If an object’s velocity is decreasing, that means it is slowing down. This can be due to a number of factors, such as friction, air resistance, or gravity. The position of an object is a measure of its location in space. If an object’s velocity is decreasing, its position will change as well. The exact way in which the position changes will depend on the object’s initial velocity and the rate at which it is decelerating.

How Does Velocity Affect Position?
The relationship between velocity and position can be described by the following equation:
position = initial position + (velocity * time)
This equation tells us that the position of an object is equal to its initial position plus the product of its velocity and the time that has elapsed. If an object’s velocity is decreasing, the term (velocity * time) will become smaller and smaller. This means that the object’s position will change less and less over time.
How to Calculate Position if Velocity is Decreasing
If you know the initial velocity of an object and the rate at which it is decelerating, you can use the following equation to calculate its position at any given time:
position = initial position + (initial velocity * time) - (0.5 * deceleration * time^2)
This equation includes an additional term, (0.5 * deceleration * time^2), which accounts for the fact that the object’s velocity is decreasing. The deceleration is a measure of how quickly the object’s velocity is decreasing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the position of an object if its velocity is decreasing, there are a few common mistakes to avoid:
- Using the wrong equation. If the object’s velocity is decreasing, you must use the equation that includes the deceleration term.
- Using the wrong sign for the deceleration. The deceleration is always a negative number. If you use a positive number for the deceleration, you will get the wrong answer.
- Forgetting to square the time. The time term in the deceleration equation must be squared. If you forget to square the time, you will get the wrong answer.
How to Step-by-Step Approach
To calculate the position of an object if its velocity is decreasing, follow these steps:
- Identify the initial velocity of the object.
- Identify the deceleration of the object.
- Identify the time that has elapsed.
- Substitute the values into the equation: position = initial position + (initial velocity * time) – (0.5 * deceleration * time^2).
- Solve for the position.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about how to calculate the position of an object if its velocity is decreasing:
-
What if the initial velocity is zero?
If the initial velocity is zero, the position of the object will not change. -
What if the deceleration is zero?
If the deceleration is zero, the object will continue to move at a constant velocity. -
What if the time is negative?
If the time is negative, the object will be moving in the opposite direction.
Conclusion
Calculating the position of an object if its velocity is decreasing is a relatively simple process. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can avoid common mistakes and get the correct answer.