Sociology Concepts
1. What is sociology?
– The scientific study of human society and social behavior.

2. What are the three major theoretical perspectives in sociology?
– Functionalist perspective: Society is a system of interconnected parts that work together to maintain stability.
– Conflict perspective: Society is characterized by conflict between different groups over scarce resources.
– Symbolic interactionist perspective: Society is created and maintained through the interactions of individuals.
3. What are the key concepts in functionalism?
– Social order: The stability and predictability of society.
– Social institutions: Patterns of behavior that meet basic social needs, such as family, education, and government.
– Socialization: The process by which individuals learn the norms and values of their society.
4. What are the key concepts in conflict theory?
– Social inequality: The unequal distribution of resources and power in society.
– Class conflict: The conflict between different classes over economic resources.
– Social change: The process by which society evolves over time.
5. What are the key concepts in symbolic interactionism?
– Meaning: The subjective interpretation of symbols and gestures by individuals.
– Social interaction: The exchange of symbols and gestures between individuals.
– Social construction of reality: The process by which individuals create and maintain a shared understanding of the world.
Social Institutions
6. What are the major social institutions?
– Family: The primary unit of socialization.
– Education: The institution responsible for transmitting knowledge and skills.
– Government: The institution responsible for maintaining order and providing services.
– Economy: The institution responsible for producing and distributing goods and services.
– Religion: The institution responsible for providing spiritual guidance and community.
7. What are the functions of the family?
– Provides physical and emotional support.
– Socializes children.
– Regulates sexual behavior.
– Produces and maintains the labor force.
8. What are the functions of education?
– Transmits knowledge and skills.
– Socializes individuals into the workforce.
– Promotes social mobility.
– Provides a foundation for lifelong learning.
9. What are the functions of government?
– Maintains order and protects citizens.
– Provides public services, such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
– Regulates the economy.
10. What are the functions of the economy?
– Produces and distributes goods and services.
– Provides jobs and income.
– Creates wealth.
11. What are the functions of religion?
– Provides spiritual guidance and community.
– Offers a sense of purpose and meaning.
– Regulates behavior.
Social Problems
12. What are the major social problems facing society today?
– Poverty: The lack of basic resources, such as food, shelter, and income.
– Crime: The violation of laws that harm individuals or society.
– Inequality: The uneven distribution of resources and power in society.
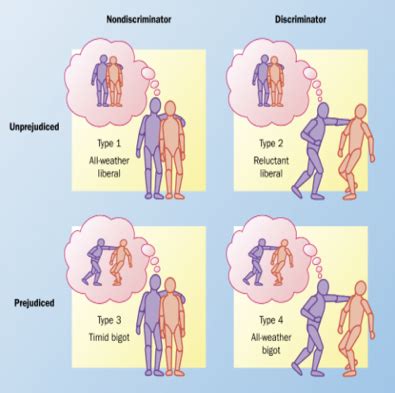
– Discrimination: The unfair treatment of individuals based on their race, gender, or other characteristics.
– Environmental degradation: The damage to the natural environment caused by human activities.
13. What are the causes of poverty?
– Lack of education and skills.
– Job loss and unemployment.
– Discrimination.
– Government policies that favor the wealthy.
– Personal circumstances, such as illness or disability.
14. What are the consequences of poverty?
– Hunger and malnutrition.
– Homelessness and lack of access to basic services.
– Poor health and mental health.
– Limited educational and economic opportunities.
– Increased crime and violence.
15. What are the solutions to poverty?
– Increasing access to education and skills training.
– Creating jobs and providing unemployment benefits.
– Reducing discrimination.
– Reforming government policies to favor the poor.
– Providing financial assistance, such as food stamps and housing vouchers.
Social Change
16. What are the major theories of social change?
– Evolutionary theory: Society evolves gradually over time through a process of natural selection.
– Revolutionary theory: Society changes abruptly through revolutions, which are caused by conflict between different groups.
– Cyclical theory: Society goes through a cycle of birth, growth, decay, and renewal.
17. What are the factors that contribute to social change?
– Technological change: The development of new technologies, such as the printing press and the internet.
– Economic change: The shift from an agricultural economy to an industrial economy to a service economy.
– Political change: The rise and fall of governments and the implementation of new policies.
– Cultural change: The emergence of new values, norms, and beliefs.
– Demographic change: The change in population size, composition, and distribution.
18. What are the consequences of social change?
– Both positive and negative consequences.
– Positive consequences include increased economic growth, improved quality of life, and greater social equality.
– Negative consequences include social disruption, economic inequality, and environmental degradation.
19. How can we manage social change?
– Plan for social change by anticipating future changes and developing strategies to mitigate their negative consequences.
– Adapt to social change by changing our behavior and institutions to meet new challenges.
– Resist social change by opposing changes that we believe are harmful to society.
20. What is the future of sociology?
– Sociology is a growing field with a bright future.
– Sociologists are needed to study the social problems facing society today and to develop solutions for these problems.
– Sociology will continue to be a vital discipline for understanding human society and social behavior.