Navigating the complex world of financial aid can be a daunting task, especially when considering the impact of your enrollment status on your eligibility. Whether you decide to pursue your education full-time or part-time, understanding the differences in financial aid options is crucial for making informed decisions about your future.

Understanding Financial Aid Eligibility
Financial aid is typically awarded based on financial need, as determined by the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). The FAFSA collects information about your family’s income and assets to calculate your Expected Family Contribution (EFC). This number is then used to determine your eligibility for various types of financial aid, including grants, scholarships, loans, and work-study.
Full-Time vs. Part-Time Enrollment
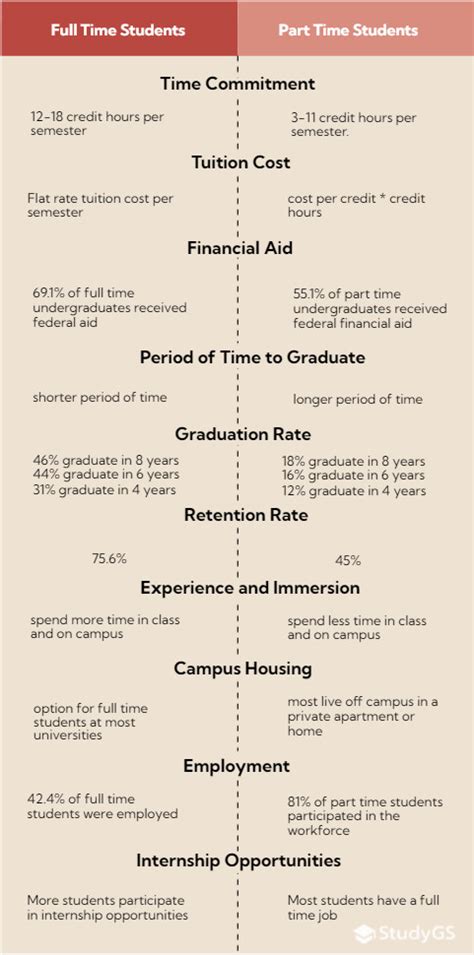
Your enrollment status, either full-time or part-time, significantly impacts your financial aid eligibility. The definition of full-time and part-time varies depending on the institution and program. Generally, full-time status requires taking a minimum of 12 credit hours per semester, while part-time status is typically defined as taking fewer than 12 credit hours.
Financial Aid for Full-Time Students
Full-time students are generally eligible for the full range of financial aid options, including:
- Grants: Grants are free money that does not need to be repaid. The most common grant program for undergraduate students is the Federal Pell Grant, awarded to students with exceptional financial need.
- Scholarships: Scholarships are also free money but are typically awarded based on merit or other specific criteria.
- Loans: Loans are borrowed money that must be repaid with interest. Federal student loans have low interest rates and flexible repayment options.
- Work-Study: Work-Study allows students to earn money to help pay for their education by working on campus.
Financial Aid for Part-Time Students
Part-time students are also eligible for financial aid, but their eligibility may be limited compared to full-time students. The types of aid available include:
- Federal Pell Grant: Part-time students may be eligible for a prorated Pell Grant based on their enrollment status.
- Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (SEOG): SEOG is a need-based grant program specifically for part-time students.
- Federal Work-Study: Part-time students may be eligible for Work-Study as long as they meet the other eligibility requirements.
It’s important to note that part-time students may receive a smaller amount of financial aid compared to full-time students, as their financial need is typically calculated based on a lower cost of attendance.
Financial Aid Impact on Cost of Education
Your enrollment status not only affects your financial aid eligibility but also impacts the overall cost of your education. Full-time students typically pay a higher tuition rate than part-time students, but they may also qualify for more financial aid. Part-time students may save money on tuition but may have to pay for their education over a longer period, which could result in higher total costs.
To determine the best financial aid option for you, it’s essential to carefully consider your financial situation and educational goals. By weighing the pros and cons of full-time vs. part-time enrollment, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial needs and academic ambitions.
Tables for Comparison
The following tables provide a detailed comparison of financial aid eligibility and the impact of enrollment status:
| Type of Financial Aid | Full-Time Students | Part-Time Students |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Pell Grant | Eligible for full grant amount | Eligible for prorated amount |
| Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (SEOG) | Eligible | Eligible |
| Federal Work-Study | Eligible | Eligible |
| Federal Direct Loans | Eligible for full amount | Eligible, but may receive a smaller amount |
| Cost Comparison | Full-Time | Part-Time |
|---|---|---|
| Tuition | Higher tuition rate | Lower tuition rate |
| Financial Aid | Typically more financial aid available | Typically less financial aid available |
| Total Cost | May be higher | May be lower over a shorter period |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When applying for financial aid, it’s important to avoid common mistakes that could impact your eligibility or the amount of aid you receive. Here are some tips to consider:
- Don’t wait to file the FAFSA. The FAFSA is available on October 1st each year, and the deadline varies depending on the state and institution. Early submission is crucial as some financial aid is awarded on a first-come, first-served basis.
- Don’t overestimate your income or assets. Be honest and accurate when reporting your family’s income and assets on the FAFSA. Overestimating your financial resources could reduce your eligibility for financial aid.
- Don’t ignore scholarship opportunities. Explore various scholarship opportunities, both through your school and external organizations. Many scholarships are available for students of all backgrounds and academic achievements.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help. If you need assistance completing the FAFSA or have questions about financial aid, don’t hesitate to contact your school’s financial aid office. They are there to help you navigate the process.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences in financial aid eligibility and implications of full-time vs. part-time enrollment is essential for making informed decisions about your education. By carefully considering your financial situation and educational goals, you can determine the best path towards achieving your academic aspirations without overwhelming financial burdens. Remember, financial aid is available to help you succeed, so take advantage of the opportunities and resources available to you.