Introduction

In the realm of evolutionary biology, natural selection reigns supreme as a driving force underpinning the remarkable diversity and adaptations observed throughout the natural world. It plays a pivotal role in Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, which serves as a cornerstone of AP Psychology.
Definition of Natural Selection
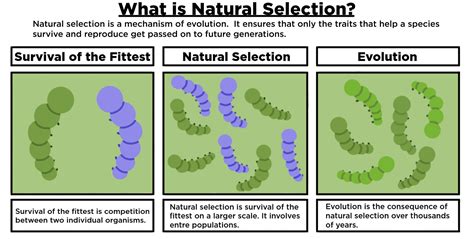
Natural selection is a process by which organisms with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in their environment are more likely to pass on their genes to subsequent generations. Consequently, these beneficial traits become more prevalent within the population over time.
Historical Context
The idea of natural selection was first proposed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in the 19th century. Their seminal work, “On the Origin of Species,” elucidated the fundamental principles of evolution through natural selection.
Mechanism of Natural Selection
The mechanism of natural selection involves the following key steps:
1. Variation: Within any population, individuals exhibit variations in their traits, which can be inherited or acquired.
2. Overproduction: Organisms tend to produce more offspring than can survive and reproduce in a given environment, leading to competition for resources.
3. Selective Pressure: The environment exerts selective pressure on organisms, favoring those with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success.
4. Differential Survival and Reproduction: Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and produce more offspring, passing on their traits to the next generation.
5. Gradual Change: Over generations, the accumulation of advantageous traits in a population leads to gradual evolutionary change.
Evidence for Natural Selection
Numerous lines of evidence support the theory of natural selection. These include:
- Fossil Record: The fossil record provides a glimpse into the evolutionary history of species, showing changes in traits over time.
- Comparative Anatomy: Comparing the anatomical structures of different species reveals similarities that suggest common ancestry.
- Molecular Biology: Genetic studies demonstrate the genetic similarities between species and the gradual changes that occur over time.
- Artificial Selection: Artificial breeding experiments, such as selective breeding in dogs, illustrate how specific traits can be passed down and intensified.
Applications of Natural Selection
The principles of natural selection have far-reaching implications and applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine: Understanding natural selection aids in developing treatments for diseases that result from genetic variations.
- Agriculture: Selective breeding techniques based on natural selection principles improve crop yields and livestock productivity.
- Conservation: Natural selection insights guide conservation efforts by identifying traits that contribute to species’ survival.
- Education: Natural selection serves as a fundamental concept in science education, fostering an understanding of the evolution of life.
Tables
Table 1: Key Components of Natural Selection
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Variation | Differences in traits among individuals |
| Overproduction | Production of more offspring than can survive |
| Selective Pressure | Environmental factors favoring certain traits |
| Differential Survival and Reproduction | Survival and reproduction of individuals with advantageous traits |
| Gradual Change | Accumulation of beneficial traits over generations |
Table 2: Evidence for Natural Selection
| Evidence | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fossil Record | Changes in species’ traits over time |
| Comparative Anatomy | Similarities in anatomical structures across species |
| Molecular Biology | Genetic relatedness and gradual genetic changes |
| Artificial Selection | Selective breeding of desired traits |
Table 3: Applications of Natural Selection
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Medicine | Development of treatments for genetic diseases |
| Agriculture | Selective breeding for improved crop yields |
| Conservation | Identification of traits contributing to species’ survival |
| Education | Fostering an understanding of evolution |
Table 4: Benefits and Limitations of Natural Selection
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Explains diversity and adaptations | Can be a slow process |
| Validated by multiple lines of evidence | Subject to environmental variation |
| Provides insights into evolutionary processes | May not account for all evolutionary changes |
Tips and Tricks
- Focus on grasping the core concept of natural selection: the survival and reproductive success of organisms with advantageous traits.
- Utilize visual representations and examples to enhance comprehension.
- Explore historical and modern evidence supporting natural selection.
- Consider the applications of natural selection in various fields to expand your understanding.
- Engage in discussions and group work to deepen your insights.
Conclusion
Natural selection remains a fundamental concept in AP Psychology, providing a powerful lens through which to understand the evolution of life and the adaptations that drive diversity. By grasping the mechanisms and implications of natural selection, individuals can appreciate the intricacies of the natural world and its continuous state of flux.