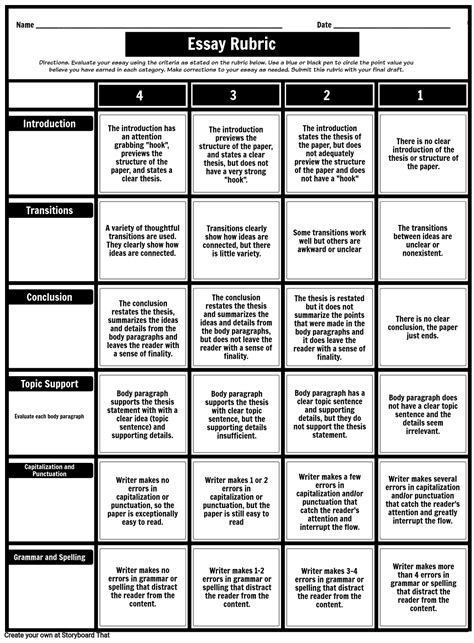
In the realm of academia, crafting well-written essays, reports, and research papers is an essential skill. To guide students in their writing endeavors, educators often employ rubrics, providing a structured framework for assessing writing quality. These rubrics offer clear criteria against which written work is evaluated, ensuring consistency and fairness in grading.

Understanding the Elements of a Rubric
Typically, a rubric comprises several components:
- Content and Organization: Assesses the depth of knowledge, logical flow, and organization of the written piece.
- Use of Evidence: Evaluates the student’s ability to support their claims using relevant evidence from sources or personal experiences.
- Language and Conventions: Focuses on the clarity, accuracy, and mechanics of the writing, including grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
Types of Rubrics for Writing
Rubrics can vary in their format and level of detail, depending on the writing task and the educational level. Some common types include:
- Analytic Rubrics: Provide detailed feedback on specific aspects of the writing, such as structure, content, and language.
- Holistic Rubrics: Offer a more general evaluation of the writing’s overall quality, providing a single score or grade.
- Checklist Rubrics: List specific criteria that students must meet, with a checkmark indicating whether each criterion is met or not.
Rubric Examples for Specific Writing Tasks
To illustrate the application of rubrics, here are some examples tailored to different types of writing assignments:
Argumentative Essay
| Criteria | Level 1 (Poor) | Level 2 (Fair) | Level 3 (Good) | Level 4 (Excellent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content and Organization | Weak or irrelevant arguments, poor organization | Somewhat relevant arguments, moderate organization | Sound arguments, clear organization | Well-supported, convincing arguments, excellent organization |
| Use of Evidence | No evidence or sources cited | Limited evidence, some sources cited | Relevant evidence from reputable sources | Extensive evidence, credible sources |
| Language and Conventions | Numerous grammar and spelling errors, unclear language | Occasional grammar and spelling errors, clear language | Minor grammar and spelling errors, precise language | No grammatical errors, sophisticated language |
Research Paper
| Criteria | Level 1 (Poor) | Level 2 (Fair) | Level 3 (Good) | Level 4 (Excellent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content and Organization | Lack of research, disorganized structure | Some research, structure somewhat clear | In-depth research, well-organized structure | Extensive research, highly organized structure |
| Use of Evidence | Plagiarized or fabricated data, no citations | Limited original research, few citations | Original research, accurate citations | Extensive original research, proper attribution |
| Language and Conventions | Errors in citation format, unclear language | Occasional errors in citation format, clear language | Consistent citation format, clear language | Flawless citation format, sophisticated language |
Creative Writing
| Criteria | Level 1 (Poor) | Level 2 (Fair) | Level 3 (Good) | Level 4 (Excellent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content and Organization | Unoriginal plot, disjointed structure | Somewhat original plot, basic structure | Engaging plot, well-developed structure | Highly original plot, intricate structure |
| Language and Conventions | Unclear imagery, awkward sentence structure | Occasional unclear imagery, some awkward sentences | Vivid imagery, varied sentence structure | Rich imagery, sophisticated sentence structure |
| Character Development | Flat characters, undeveloped personalities | Somewhat developed characters, distinct traits | Well-developed characters, complex personalities | Fully realized characters, nuanced personalities |
Strategies for Using Rubrics Effectively
To maximize the effectiveness of rubrics, consider the following strategies:
- Provide Clear and Concise Instructions: Explain the purpose and expectations of the rubric to students.
- Involve Students in the Process: Engage students in the creation or review of the rubric to foster their understanding.
- Use Rubrics for Self-Assessment: Encourage students to self-assess their writing using the rubric for self-reflection.
- Offer Timely Feedback: Provide regular feedback based on the rubric to help students identify areas for improvement.
- Review and Revise Rubrics: Periodically review and revise rubrics as needed to ensure they align with academic standards and best practices.
Tips and Tricks for Exceptional Writing
In addition to using rubrics, consider these tips and tricks to enhance your writing skills:
- Read Widely: Explore various genres and writing styles to broaden your vocabulary and understanding of effective writing.
- Plan and Outline: Create an outline before writing to organize your thoughts and ensure logical flow.
- Craft Strong Introductions and Conclusions: Engage readers with a captivating opening sentence and summarize key points effectively in the conclusion.
- Use Transition Words: Connect ideas smoothly and improve readability by using appropriate transition words.
- Proofread Carefully: Take time to proofread your work thoroughly for any errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How do I choose the right rubric for my writing task?
A: Consider the type of writing assignment, the grade level of the students, and the specific learning objectives to select an appropriate rubric.
Q2: Can I use rubrics for different purposes?
A: Yes, rubrics can be used for assessment, self-assessment, and feedback purposes.
Q3: What is the most important element of a rubric?
A: The content and organization section, as it assesses the substance and structure of the writing.
Q4: How often should I use rubrics?
A: Rubrics should be used consistently throughout the writing process, from planning to grading.
Q5: What are some effective strategies to improve my writing scores?
A: Regularly practice writing, seek constructive feedback, and utilize writing resources such as grammar checkers and writing centers.
Q6: How can I stay updated with the latest writing best practices?
A: Attend workshops, read professional journals, and consult with experts in the field of writing to continue your growth.