Introduction
AP Physics 2 is a challenging but rewarding course that explores the fundamental principles of electricity, magnetism, fluids, and thermodynamics. Many students find themselves seeking additional support to enhance their understanding and preparation for the AP exam. This article aims to provide an in-depth review of AP Physics 2, covering all the essential topics tested on the exam.

Concepts and Equations
Electrostatics
- Electric charges and Coulomb’s law
- Electric fields and potential energy
- Conductors, insulators, and polarization
- Capacitors and dielectric materials
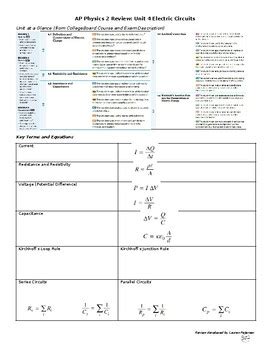
Circuits
- Ohm’s law and circuit analysis
- Resistors, capacitors, and inductors
- DC and AC circuits
- Kirchhoff’s laws
Magnetism
- Magnetic fields and forces
- Ampère’s law
- Faraday’s law of induction
- Electromagnets and transformers
Fluids
- Fluid density and pressure
- Buoyancy and Archimedes’ principle
- Fluid dynamics and Bernoulli’s equation
- Viscous flow and Reynolds number
Thermodynamics
- Heat, temperature, and specific heat
- Laws of thermodynamics
- Entropy and heat engines
- Thermal expansion and gas laws
Problem-Solving Strategies
Solving AP Physics 2 problems requires a systematic approach. Here are some key strategies:
- Identify the givens and what the problem asks for.
- Draw a diagram to visualize the situation.
- Apply relevant equations and concepts.
- Use algebra, trigonometry, or vector analysis as needed.
- Check your units and the reasonableness of your answer.
Practice and Preparation
Practice Problems
Numerous practice problems are available online and in textbooks. Solving these problems is essential for building proficiency in applying concepts.
AP Style Questions
The AP Physics 2 exam consists of multiple-choice questions, free-response questions, and a lab component. The College Board provides official practice exams and resources to familiarize students with the exam format.
Review Sessions
Attend review sessions offered by your school or online to reinforce concepts and ask questions.
Study Groups
Form study groups with classmates to collaborate on problem-solving and discuss challenging topics.
Sample Questions with Explanations
Question 1: A positive charge of 1 μC is located at the origin. What is the electric field at a point (2, 3) m away?
Answer:
| Given Values | Equation | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| q = 1 μC | E = k * q / r^2 | E = (9 x 10^9 Nm^2/C^2) * (1 x 10^-6 C) / (5 m)^2 |
| r = 5 m | | |
| | | E = 3600 N/C |
Question 2: A 10 Ohm resistor is connected to a 5 Volt battery. What is the current flowing through the circuit?
Answer:
| Given Values | Equation | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| V = 5 V | I = V / R | I = 5 V / 10 Ohm |
| R = 10 Ohm | | |
| | | I = 0.5 A |
Question 3: A cylindrical water tank with a radius of 1 m and a height of 2 m is filled with water. What is the pressure at the bottom of the tank?
Answer:
| Given Values | Equation | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| ρ = 1000 kg/m^3 | P = ρ * g * h | P = (1000 kg/m^3) * (9.8 m/s^2) * (2 m) |
| g = 9.8 m/s^2 | | |
| h = 2 m | | |
| | | P = 19600 Pa |
Conclusion
Mastering AP Physics 2 requires a strong understanding of concepts, problem-solving skills, and consistent practice. By utilizing the resources and strategies outlined in this article, students can prepare effectively for the AP exam and lay a solid foundation for further studies in physics and engineering.