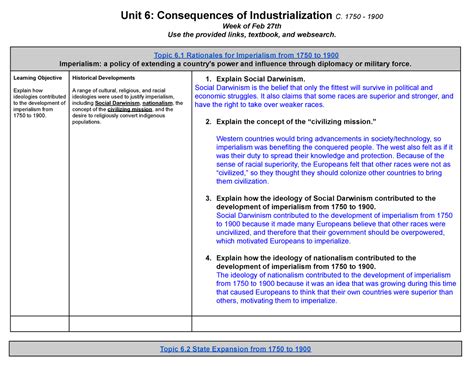
Introduction

Unit 6 of the AP World History curriculum delves into the pivotal period of European global supremacy, spanning from the 15th to the 19th centuries. This transformative era witnessed an unprecedented expansion of European influence and the emergence of global empires. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the key factors that propelled European powers to global dominance and the profound impact it had on the world.
The Age of Exploration
The advent of the Age of Exploration in the 15th century marked a turning point in global history. European powers such as Portugal and Spain embarked on daring maritime expeditions, seeking new trade routes and resources. Driven by a thirst for wealth and prestige, they ventured into uncharted waters, leading to significant geographical discoveries.
Technological Advancements
Technological innovations played a pivotal role in European expansion. The development of the compass, astrolabe, and caravel ships enabled navigators to venture farther and more accurately. The invention of cannons and muskets provided European armies with a decisive military advantage.
Economic Motivations
The pursuit of economic gain was a primary driving force behind European expansion. The discovery of new lands brought access to valuable goods such as spices, gold, and silver. European merchants established trading posts and colonies to secure these resources, leading to the rise of mercantilism and the accumulation of vast wealth.
Political and Religious Factors
Political and religious factors also contributed to European expansion. The growth of nation-states and the search for new territories fueled competition among European powers. Religious zeal, particularly the spread of Christianity, provided an ideological justification for colonization and the establishment of missions.
The Impact of European Expansion
The rise of European global supremacy had profound consequences for the world. It resulted in:
- Globalization: The exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between Europe and the rest of the world intensified, leading to the emergence of a globalized world.
- Colonization: European powers established colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, exploiting their natural resources and imposing their political and economic systems.
- Indigenous Displacement: European colonization often led to the displacement and subjugation of indigenous populations, resulting in cultural loss and social upheaval.
- Slave Trade: The transatlantic slave trade emerged as a brutal and inhumane practice, forcibly transporting millions of Africans to the Americas to serve as labor.
The Legacy of European Global Supremacy
The legacy of European global supremacy is complex and multifaceted. It shaped the geopolitical landscape of the world, creating new power dynamics and economic inequalities. It also led to cultural exchanges, the spread of Western ideas, and the emergence of global institutions.
Assessment Table: Key Factors in European Expansion
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Technological Advancements | Developments such as the compass, astrolabe, and caravel ships |
| Economic Motivations | Pursuit of wealth through trade and colonization |
| Political and Religious Factors | Competition among nation-states and spread of Christianity |
Chronological Table: European Colonization Timeline
| Century | Event |
|---|---|
| 15th | Portuguese exploration of West Africa |
| 16th | Spanish colonization of the Americas |
| 17th | British and French establishment in North America |
| 18th | British dominance in India |
| 19th | European powers carve up Africa |
Infographic: The Transatlantic Slave Trade
- Estimated 12.5 million Africans forcibly transported to the Americas
- Majority transported to Brazil, the Caribbean, and the United States
- Slave trade peaked in the 18th century
Case Study: The Indian Mutiny of 1857
The Indian Mutiny of 1857 was a major uprising against British rule in India. It highlighted the growing resentment and resistance to European colonial rule, ultimately contributing to India’s struggle for independence.
Conclusion
Unit 6 AP World History provides a comprehensive examination of the rise of European global supremacy. Driven by technological advancements, economic motives, political ambitions, and religious ideologies, European powers expanded their influence across the globe, shaping the course of world history. The legacy of this era continues to influence contemporary geopolitics, economic disparities, and cultural exchanges. understanding this pivotal period is essential for students seeking a deeper comprehension of our interconnected world.