Introduction
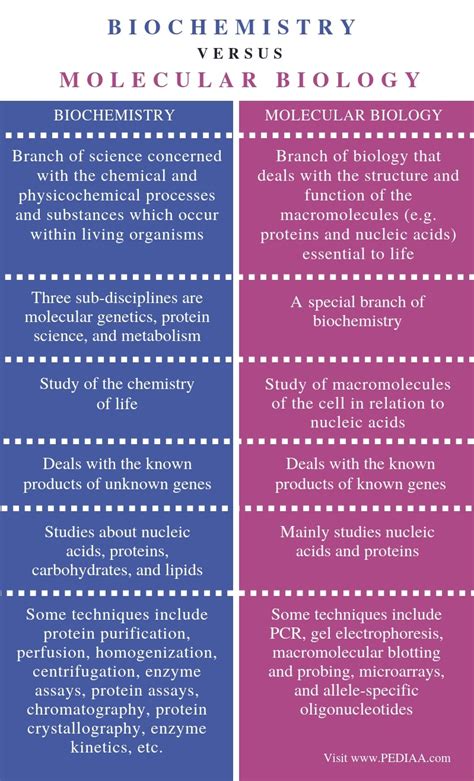
The fields of biochemistry and biological sciences are closely intertwined, yet distinct disciplines that share a common foundation in the study of living organisms. While biological sciences encompass a broad range of subfields, including zoology, botany, microbiology, and ecology, biochemistry focuses specifically on the chemical processes and reactions that occur within living systems.

Scope and Focus
Biological sciences delve into the structure, function, and behavior of organisms at various levels of organization, from molecules to ecosystems. It explores the diversity of life, evolutionary processes, and the interactions between organisms and their environments. In contrast, biochemistry concentrates on the chemical basis of life, examining the molecules, enzymes, and metabolic pathways that underpin the functioning of living cells.
Methodologies
Both biological sciences and biochemistry employ a combination of experimental and theoretical approaches. Biological sciences often involve field studies, observational experiments, and comparative analyses. Biochemistry, on the other hand, relies heavily on laboratory techniques such as spectroscopy, chromatography, and molecular biology tools to investigate the structure and function of biological molecules.
Key Concepts
Biological Sciences:
- Evolution and natural selection
- Genetic inheritance
- Biodiversity and ecological interactions
- Cell biology and development
- Evolutionary history and systematics
Biochemistry:
- Enzyme catalysis and metabolic pathways
- Nucleic acid structure and gene expression
- Protein structure and function
- Bioenergetics and energy metabolism
- Molecular basis of disease
Applications
Biological Sciences:
- Medicine and healthcare
- Agriculture and food production
- Environmental conservation
- Biotechnology and drug development
- Forensic science
Biochemistry:
- Pharmaceutical development
- Nutritional science
- Clinical diagnostics
- Biotechnology and genetic engineering
- Biomaterials design
Career Paths
Individuals with education in biological sciences can pursue careers as:
- Biologists
-Ecologists - Zoologists
- Botanists
- Microbiologists
Careers in biochemistry include:
- Biochemists
-Molecular biologists - Pharmaceutical scientists
- Biotechnology engineers
- Clinical laboratory scientists
Research Funding
According to the National Science Foundation (NSF), biological sciences received $7.6 billion in federal research funding in 2021, while biochemistry accounted for $3.1 billion. These figures reflect the substantial investment in both fields.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mistaking Biochemistry for Biology: While biochemistry is a subfield of biological sciences, it is a distinct discipline with its own unique focus on chemical processes.
Assuming Biological Sciences is Only for Scientists: Biological sciences encompass a wide range of non-scientific applications, including conservation, agriculture, and healthcare.
Conclusion
Biochemistry and biological sciences are complementary fields that provide essential insights into the nature and functioning of living systems. By understanding the distinctions and synergies between these disciplines, researchers, students, and practitioners can advance scientific knowledge and develop innovative solutions to societal challenges.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a biochemist and a biologist?
– A biochemist specializes in the chemical processes of living cells, while a biologist studies the structure, function, and behavior of organisms.
2. Can I work in both biochemistry and biological sciences?
– Yes, it is possible to pursue a career that combines elements of both fields. Interdisciplinary research and industry roles often require expertise in both areas.
3. Which field has more job opportunities?
– Both biochemistry and biological sciences offer a range of job opportunities. The specific availability of positions may vary depending on factors such as location, industry, and experience.
4. How can I prepare for a career in biochemistry or biological sciences?
– Strong academic performance in science and math is essential. Consider pursuing a bachelor’s degree in biochemistry, biology, or a related field.
5. Is it possible to switch careers from one field to the other?
– With additional education and experience, it is possible to transition between biochemistry and biological sciences. Consider taking courses or pursuing a graduate degree in the desired field.
6. How do biochemistry and biological sciences contribute to society?
– Both fields play a vital role in advancing healthcare, agriculture, environmental conservation, and industrial applications.