Beneath our feet, hidden from plain sight, lies a vital resource that sustains life on Earth: aquifers. These vast underground reservoirs of water play a crucial role in our ecosystems, providing drinking water, supporting agriculture, and regulating the environment.

What is an Aquifer?
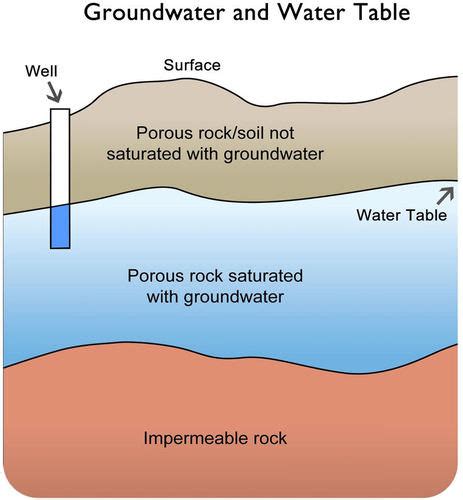
An aquifer is a layer or formation of rock, soil, or sand that holds water and allows it to flow. Aquifers typically occur in layers between impermeable layers of rock or clay that prevent water from escaping. The water in an aquifer is stored in the spaces between the grains of rock or soil and moves slowly through the aquifer under the influence of gravity.
The Importance of Aquifers
Aquifers are essential for human civilization. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), groundwater from aquifers provides drinking water for over 2 billion people worldwide. Aquifers also support irrigation systems, which account for approximately 70% of global freshwater withdrawals for agriculture.
Beyond their direct use, aquifers play a crucial role in maintaining the environment. They regulate streamflow, support wetlands, and provide habitat for aquatic plants and animals. Aquifers also help mitigate droughts and floods by storing excess water and releasing it gradually during dry periods.
The Threats to Aquifers
Aquifers face a number of threats, including:
- Over Pumping: Excessive groundwater extraction can deplete aquifers, leading to shortages, subsidence, and saltwater intrusion.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities can contaminate aquifers with chemicals, heavy metals, and other pollutants.
- Climate Change: Changes in precipitation patterns and rising sea levels can alter the recharge and storage capacity of aquifers.
Protecting Our Aquifers
Protecting and managing aquifers is essential for ensuring their long-term sustainability. This requires:
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of groundwater levels and quality is crucial for detecting potential problems early.
- Regulation: Setting and enforcing groundwater extraction limits is necessary to prevent over pumping.
- Pollution Prevention: Implementing best practices in agriculture, industry, and waste management can minimize the risk of aquifer contamination.
- Artificial Recharge: Injecting treated wastewater or stormwater into aquifers can help replenish depleted groundwater reserves.
Aquifers: A Source of Innovation
The importance of aquifers has inspired innovative approaches to water management. For example, “Aquifer Storage and Recovery” (ASR) involves storing treated wastewater or stormwater in aquifers for later use during droughts or other periods of water scarcity.
Another promising technology is “Aquifer Thermal Energy Storage” (ATES), which uses aquifers to store excess heat from buildings or industrial processes for use in heating or cooling systems.
Conclusion
Aquifers are an invaluable resource that supports life on Earth. By recognizing their importance and implementing measures to protect and manage them, we can ensure their continued sustainability for generations to come. Remember, the water we drink today may have been stored in an aquifer thousands of years ago – let’s value this precious resource and safeguard it for the future.
Useful Tables
Table 1: Global Groundwater Withdrawals
| Sector | Withdrawal (billion m³/year) |
|—|—|—|
| Drinking Water | 240 |
| Agriculture | 1,740 |
| Industry | 260 |
| Other | 150 |
Table 2: Aquifer Recharge Rates
| Aquifer Type | Recharge Rate (mm/year) |
|—|—|—|
| Unconfined Aquifer | 10-100 |
| Confined Aquifer | 0.1-10 |
Table 3: Aquifer-Dependent Ecosystems
| Ecosystem | Description |
|—|—|—|
| Wetlands | Coastal areas, swamps, marshes |
| Springs | Areas where groundwater flows out of the ground |
| Seeps | Areas where groundwater oozes out of the ground |
Table 4: Innovative Aquifer Technologies
| Technology | Description |
|—|—|—|
| Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) | Storing water in aquifers for later use |
| Aquifer Thermal Energy Storage (ATES) | Storing heat in aquifers for use in heating or cooling systems |
| Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) | Enhancing aquifer recharge by injecting treated wastewater or stormwater |