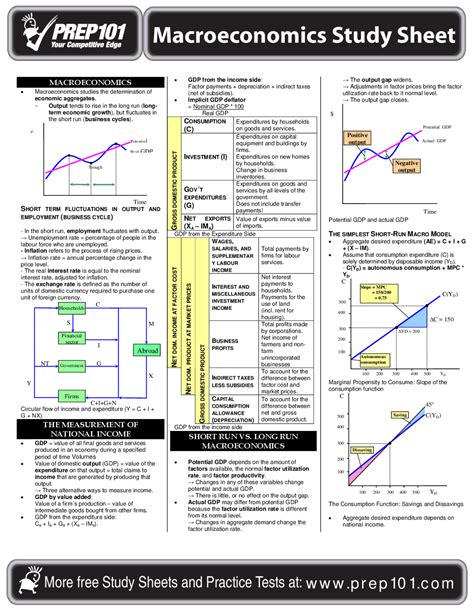
Introduction: Dominating the AP Macro Exam
Mastering Advanced Placement (AP) Macroeconomics requires a comprehensive understanding of economic principles and analytical skills. This cheat sheet serves as your ultimate study guide, providing a concise and effective review of essential concepts and exam tips.

National Income Accounting: Measuring the Economy’s Health
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product): Total value of all final goods and services produced in a country within a year.
- GNP (Gross National Product): GDP plus income earned by nationals abroad.
- Disposable Personal Income (DPI): Income available to households after taxes and other deductions.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): Measures inflation by tracking price changes in a fixed basket of goods and services.
Economic Growth and Economic Indicators
- Real GDP Growth Rate: Percentage change in GDP adjusted for inflation.
- Unemployment Rate: Percentage of the labor force actively seeking work without success.
- Inflation Rate: Percentage change in the CPI over time.
- Productivity: Output per hour worked, a key indicator of economic efficiency.
Monetary and Fiscal Policy: Shaping the Economy
Monetary Policy (Federal Reserve):
– Open Market Operations (OMO): Buying or selling government securities to increase or decrease the money supply.
– Reserve Requirements: Minimum amount of reserves banks must hold, affecting the money supply.
– Discount Rate: Interest rate banks pay to borrow from the Federal Reserve.
Fiscal Policy (Government):
– Government Spending: Direct spending on goods and services, stimulating the economy.
– Taxation: Levies on income, consumption, or wealth, affecting disposable income and incentives.
Aggregate Demand and Supply: Balancing the Economy
- Aggregate Demand (AD): Total demand for goods and services in an economy.
- Aggregate Supply (AS): Total quantity of goods and services an economy can produce.
- Equilibrium: Point where AD = AS, determining price level and output.
- Shifts in AD or AS: Can lead to changes in inflation, output, or both.
International Trade and Exchange Rates
- Imports: Goods and services purchased from other countries.
- Exports: Goods and services sold to other countries.
- Trade Deficit: When imports exceed exports.
- Exchange Rates: Prices of currencies in relation to each other.
- Balance of Payments: Record of a country’s economic transactions with the rest of the world.
Fiscal Policy in Practice: Implementing Solutions
- Expansionary Fiscal Policy: Increases government spending or lowers taxes, stimulating economic growth.
- Contractionary Fiscal Policy: Decreases government spending or raises taxes, reducing inflationary pressures.
- Budget Deficit: Government spending exceeds revenue.
- Budget Surplus: Government revenue exceeds spending.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing GDP with GNP or DPI.
- Oversimplifying inflation as a general price increase.
- Neglecting the role of productivity in economic growth.
- Misinterpreting shifts in AD and AS.
- Ignoring the impact of international trade on the economy.
Why AP Macroeconomics Matters
- Economic Literacy: Understands how economies function and make informed decisions.
- Career Preparation: Opens doors to careers in finance, economics, and policymaking.
- Critical Thinking Skills: Enhances analytical and problem-solving abilities.
- Citizenship Involvement: Equips students to engage in public discourse on economic issues.
Benefits of Studying with This Cheat Sheet
- Comprehensive Coverage: Summarizes key concepts and exam material.
- Concise and Accessible: Easy to navigate and review at a glance.
- Exam Preparation: Reinforces understanding and improves confidence.
- Time-Saving: Eliminates the need for extensive note-taking.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most important concept to master for the AP Macro exam?
National income accounting forms the foundation for understanding the economy.
2. How can I improve my understanding of monetary and fiscal policy?
Practice applying concepts to real-world scenarios and recognizing policy tools.
3. What is the most challenging topic on the exam?
Aggregate supply and demand analysis requires careful understanding of equilibrium and shifts.
4. How should I allocate my study time?
Prioritize national income accounting, monetary and fiscal policy, and aggregate demand and supply.
5. What resources are recommended for additional support?
Khan Academy, Princeton Review, and official College Board materials.
6. When should I start studying for the AP Macro exam?
Start early to allow ample time for review and practice.
7. How many practice tests should I take before the exam?
Aim for 4-6 full-length practice tests to simulate test conditions.
8. What is the best way to approach the free-response questions?
Structure responses using PIE (Point, Introduce, Explain) to provide clear and concise arguments.
Tables for Quick Reference
Table 1: Major Economic Indicators
| Indicator | Definition |
|---|---|
| GDP | Total value of all final goods and services produced in a country within a year |
| CPI | Measures inflation by tracking price changes in a fixed basket of goods and services |
| Unemployment Rate | Percentage of the labor force actively seeking work without success |
| Productivity | Output per hour worked |
Table 2: Monetary Policy Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Open Market Operations | Buying or selling government securities to increase or decrease the money supply |
| Reserve Requirements | Minimum amount of reserves banks must hold, affecting the money supply |
| Discount Rate | Interest rate banks pay to borrow from the Federal Reserve |
Table 3: Fiscal Policy Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Government Spending | Direct spending on goods and services, stimulating the economy |
| Taxation | Levies on income, consumption, or wealth, affecting disposable income and incentives |
| Budget Deficit | Government spending exceeds revenue |
| Budget Surplus | Government revenue exceeds spending |
Table 4: Impact of Shifts in AD and AS
| Shift | Effect on Price Level | Effect on Output |
|---|---|---|
| AD Increase | Increase | Increase |
| AD Decrease | Decrease | Decrease |
| AS Increase | Decrease | Increase |
| AS Decrease | Increase | Decrease |