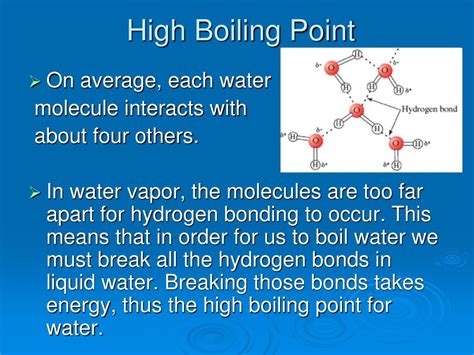
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes from a liquid to a gas. Generally, larger molecules have higher boiling points than smaller molecules. This is because larger molecules have stronger intermolecular forces, which hold the molecules together more tightly and make it more difficult for them to escape into the gas phase.

Factors Affecting Boiling Point
There are several factors that affect the boiling point of a substance, including:
- Molecular weight: As mentioned above, larger molecules generally have higher boiling points than smaller molecules. This is because larger molecules have more electrons, which create stronger intermolecular forces.
- Polarity: Polar molecules have stronger intermolecular forces than nonpolar molecules. This is because polar molecules have a positive end and a negative end, which attract each other.
- Hydrogen bonding: Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between hydrogen atoms and electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine. Hydrogen bonding is a very strong intermolecular force, and it can significantly increase the boiling point of a substance.
Boiling Points of Common Substances
The following table lists the boiling points of some common substances:
| Substance | Molecular Weight | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Helium | 4 | -268.9 |
| Methane | 16 | -161.6 |
| Water | 18 | 100 |
| Ethanol | 46 | 78.3 |
| Benzene | 78 | 80.1 |
As you can see from the table, larger molecules generally have higher boiling points. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, water has a higher boiling point than ethanol, even though ethanol is a larger molecule. This is because water molecules are polar and form hydrogen bonds, which gives them stronger intermolecular forces than ethanol molecules.
Applications of Boiling Points
The boiling point of a substance is an important property that has many applications in chemistry and industry. For example, boiling points are used to:
- Separate mixtures: Boiling points can be used to separate mixtures of liquids by distillation. Distillation is a process in which a mixture of liquids is heated until the more volatile liquid boils and evaporates. The evaporated liquid is then condensed and collected.
- Determine the purity of a substance: The boiling point of a substance can be used to determine its purity. If a substance is pure, it will have a sharp boiling point. If a substance is impure, it will have a boiling point range.
- Identify unknown substances: The boiling point of a substance can be used to help identify unknown substances. By comparing the boiling point of an unknown substance to the boiling points of known substances, it is possible to narrow down the possibilities and identify the unknown substance.
Conclusion
In general, larger molecules have higher boiling points than smaller molecules. This is because larger molecules have stronger intermolecular forces, which hold the molecules together more tightly and make it more difficult for them to escape into the gas phase. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as water, which has a higher boiling point than ethanol due to its polarity and hydrogen bonding.