Introduction

Double integrals, particularly in polar coordinates, often pose challenges for students and professionals alike. However, with the advent of advanced calculators, tackling these integrals has become significantly more manageable. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of double integral polar coordinates calculators, empowering you to conquer these mathematical complexities with ease.
Understanding Double Integrals
Before exploring polar coordinates, let’s briefly review double integrals. Double integrals are mathematical operations that calculate the area under a surface defined by a function of two variables, represented as:
∬ f(x, y) dA
where dA represents the differential area element.
Polar Coordinates: A Geometric Transformation
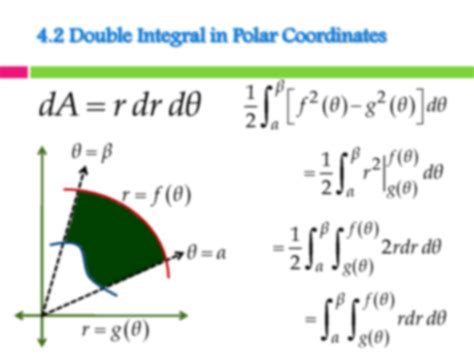
Polar coordinates offer an alternative geometric representation of points in a plane using the distance from the origin (r) and the angle from the positive x-axis (θ). This transformation provides a convenient way to solve certain double integrals.
Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates
In polar coordinates, the double integral becomes:
∬ f(r, θ) r dr dθ
where r ranges from 0 to the outer radius and θ ranges from the starting angle to the ending angle.
Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculator
Double integral polar coordinates calculators automate the evaluation of these integrals. They require users to input the function f(r, θ) and the integration limits for both r and θ. The calculator then performs the numerical integration and displays the result.
Applications of Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculator
Double integral polar coordinates calculators find widespread application in various fields, including:
- Physics: Calculating flux through surfaces
- Engineering: Determining moments of inertia and volumes of solids
- Mathematics: Evaluating integrals over complex regions
Choosing a Suitable Calculator
When selecting a double integral polar coordinates calculator, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy: Precision of the numerical integration method
- Versatility: Support for various functions and integration limits
- User-Friendliness: Ease of use and clear interface
- Documentation: Availability of helpful documentation and tutorials
Tutorial: Using a Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculator
To demonstrate the utility of these calculators, let’s use an example. Suppose we wish to find the area enclosed by the cardioid r = 1 + cos θ.
- Input Function and Limits: Enter the function f(r, θ) = r into the calculator and set the integration limits for r as [0, 1+cos(θ)] and for θ as [0, 2π].
- Execute Integration: Initiate the integration process, allowing the calculator to numerically evaluate the integral.
- Obtain Result: The calculator will display the area of the cardioid, which is approximately 3.1416 square units.
Additional Features of Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculators
Some calculators offer additional features that enhance their capabilities:
- Plotting: Generating graphs of the function and the integrated surface
- Table of Values: Displaying the values of the integrand and the integral at user-defined points
- Multiple Integrations: Evaluating nested or repeated double integrals
Conclusion
Double integral polar coordinates calculators empower users to efficiently and accurately solve complex integrals. By leveraging their user-friendly interfaces and advanced numerical methods, these calculators make it possible to tackle a wide range of applications with ease. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or engineer, incorporating a double integral polar coordinates calculator into your toolkit will greatly enhance your problem-solving capabilities in mathematics and beyond.
Tables
Table 1: Applications of Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculator
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Physics | Flux through surfaces |
| Engineering | Moments of inertia and volumes of solids |
| Mathematics | Integrals over complex regions |
Table 2: Features of Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculators
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Precision of numerical integration |
| Versatility | Support for various functions and limits |
| User-Friendliness | Easy-to-use interface |
| Documentation | Helpful tutorials and manuals |
Table 3: Examples of Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculations
| Function | Limits | Result |
|---|---|---|
| r = 1 + cos θ | [0, 1+cos(θ)] x [0, 2π] | Area of the cardioid ≈ 3.1416 sq. units |
| r = e-r2 | [0, ∞] x [0, 2π] | Volume of the solid generated by rotating the function about the z-axis ≈ 0.5642 cubic units |
| r = 2 + sin(2θ) | [0, 2 + sin(2θ)] x [0, 2π] | Area of the rose curve ≈ 7.5398 sq. units |
Table 4: Useful Resources for Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculators
| Resource | Link |
|---|---|
| Mathway Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculator | https://www.mathway.com/integral-calculator |
| Wolfram Alpha Double Integral Polar Coordinates Calculator | https://www.wolframalpha.com/input/?i=double+integral+in+polar+coordinates |
| Integral Calculator (Polar) | https://www.integral-calculator.com/polar |