The Ultimate Guide to Grading and Assessment

In the realm of education, grades hold immense significance as a measure of academic performance. Students, parents, and educators alike rely on grades to evaluate progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions. Understanding the intricacies of grading systems is crucial for students to navigate the academic landscape successfully.
This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of grading, deciphering the meaning behind a score of 39/50. We will explore the different grading scales, the factors that influence grade determination, and strategies for improving academic performance.
Understanding Grading Scales
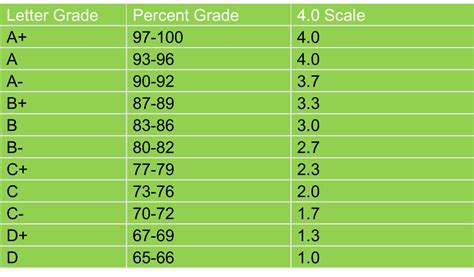
The most prevalent grading scale in use today is the 100-point scale, where assessments are assigned a numerical value between 0 and 100. Each grade range corresponds to a specific level of achievement.
Common 100-Point Grading Scale:
| Grade Range | Percentage | Letter Grade |
|---|---|---|
| 90-100 | 90% – 100% | A |
| 80-89 | 80% – 89% | B |
| 70-79 | 70% – 79% | C |
| 60-69 | 60% – 69% | D |
| 0-59 | 0% – 59% | F |
Interpreting a 39/50 Grade
Based on the 100-point grading scale, a score of 39/50 translates to:
- Percentage: 78%
- Letter Grade: C
This grade indicates a satisfactory level of achievement, meeting the minimum requirements for passing the assessment. It suggests that the student has demonstrated a basic understanding of the subject matter but may have room for improvement in certain areas.
Factors Influencing Grade Determination
Numerous factors contribute to the determination of a grade, including:
- Class Participation: Attendance, engagement in discussions, and active involvement can positively impact grades.
- Homework and Assignments: Completing assignments thoroughly and on time demonstrates a commitment to learning and earns valuable points.
- Quizzes and Tests: These assessments evaluate knowledge and comprehension of specific topics.
- Projects and Presentations: These tasks assess higher-order thinking skills, creativity, and communication abilities.
- Extra Credit: Completing additional assignments or participating in extracurricular activities can provide opportunities to earn bonus points.
Strategies for Improving Academic Performance
Enhancing academic performance requires a combination of effective study habits, time management skills, and a positive attitude. Consider the following strategies:
- Establish Realistic Goals: Set achievable targets to avoid feeling overwhelmed and maintain motivation.
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan dedicated study time slots to ensure consistent study habits.
- Take Effective Notes: Engage in active listening and note-taking during lectures to enhance comprehension and recall.
- Review Regularly: Revisit notes and materials to reinforce learning and identify areas for improvement.
- Seek Help When Needed: Do not hesitate to ask questions, attend office hours, or seek clarification from instructors or peers.
- Stay Organized: Keep track of assignments, deadlines, and notes to prevent missed opportunities or lost materials.
- Get Enough Sleep: A well-rested mind is essential for optimal learning and memory retention.
Additional Grading Systems
Beyond the 100-point scale, several other grading systems are used in educational settings:
- Percentage Grading: Assessments are graded as a percentage, with 100% representing a perfect score.
- Letter Grading: Grades are expressed as letters (A, B, C, D, F), with each letter corresponding to a specific range of percentages.
- Pass/Fail Grading: Assessments are graded simply as “Pass” or “Fail,” without specific numerical or percentage values.
- Credit/No Credit Grading: Assessments are graded as “Credit” for passing and “No Credit” for failing, without specific numerical or percentage values.
Conclusion
A grade of 39/50 is a satisfactory academic achievement that suggests a basic understanding of the subject matter. However, to truly excel in academics, students must adopt effective study strategies, seek support when needed, and continuously strive to improve their knowledge and skills. By understanding the intricacies of grading systems and implementing proven improvement strategies, students can unlock their academic potential and achieve their educational goals.