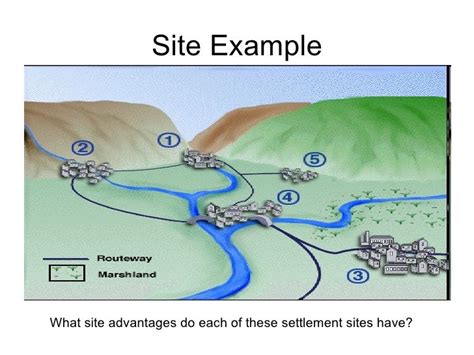
What is a Site?

In geography, a site refers to a specific location with distinct physical characteristics and attributes that make it suitable for a particular purpose. It is the smallest unit of space in geography and serves as the foundation for understanding the distribution and organization of human activities on Earth’s surface.
Key Characteristics of a Site:
- Location: The geographic position of the site, typically described by latitude and longitude or other spatial coordinates.
- Physical Attributes: The natural features of the site, including topography, soil conditions, vegetation, and water resources.
- Accessibility: The ease with which the site can be reached and accessed from various points.
- Suitability: The extent to which the site’s physical characteristics match the specific requirements of a particular activity or development.
Types of Sites:
- Natural Sites: Sites with distinctive natural features, such as mountains, rivers, lakes, and beaches.
- Cultural Sites: Sites created or modified by humans, such as historical landmarks, archaeological sites, and religious monuments.
- Functional Sites: Sites designed for a specific purpose, such as residential areas, industrial zones, or commercial centers.
- Ephemeral Sites: Sites that are temporary in nature, such as festivals or sporting events.
Factors Influencing Site Selection:
The selection of a site for a particular activity is influenced by various factors, including:
- Environmental Impact: The potential effects of the activity on the environment and the need for mitigation measures.
- Economic Viability: The costs associated with developing the site and the potential revenue it can generate.
- Social and Cultural Considerations: The compatibility of the activity with the surrounding community and its impact on local culture.
- Technological Feasibility: The availability of necessary infrastructure and resources to support the activity.
Applications of Site Analysis in Geography:
The analysis of sites is crucial in geography for understanding:
- Land Use Planning: Identifying suitable locations for various land uses, such as housing, industry, and recreation.
- Environmental Management: Assessing the environmental impact of development and implementing conservation strategies.
- Tourism and Heritage Preservation: Choosing appropriate sites for tourism activities and preserving cultural and historical assets.
- Transportation Planning: Determining the optimal location for transportation infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and airports.
- Disaster Preparedness and Mitigation: Identifying areas vulnerable to natural hazards and developing strategies to reduce risks.
Examples of Notable Sites:
- Great Barrier Reef (Australia): A vast coral reef system known for its rich biodiversity.
- Taj Mahal (India): A mausoleum built by Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife.
- Silicon Valley (USA): A region renowned for technological innovation and industry.
- Amazon Rainforest (Brazil): The largest tropical rainforest in the world, housing immense biodiversity.
- Eiffel Tower (France): An iconic structure located in Paris, one of the most visited sites in the world.
Conclusion:
A site in geography is a fundamental concept that refers to a specific location with particular characteristics that determine its suitability for various purposes. By understanding the characteristics, types, and applications of sites, geographers can effectively analyze and plan for the distribution and organization of human activities on Earth’s surface.