Introduction

Fractions, those ubiquitous mathematical expressions that represent parts of a whole, often evoke a sense of unease among learners. But fear not, for this comprehensive cheat sheet will empower you with a deep understanding of fractions, turning your mathematical woes into triumphs.
Understanding Fractions
A fraction is a number that represents a part of a whole. It consists of two parts: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). The numerator indicates the number of parts considered, while the denominator indicates the total number of parts in the whole.
Types of Fractions
- Proper Fractions: Numerator is smaller than the denominator (e.g., 1/2)
- Improper Fractions: Numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 5/2)
- Mixed Numbers: A combination of a whole number and a proper fraction (e.g., 2 1/2)
Simplifying Fractions
To simplify a fraction, divide both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common factor (GCF). This reduces the fraction to its lowest terms, making it easier to work with. For example:
- 6/12 = 2/4 = 1/2
Converting Fractions
- To Decimal: Divide the numerator by the denominator (e.g., 1/2 = 0.5)
- To Percentage: Multiply the fraction by 100 (e.g., 1/2 = 50%)
- To Mixed Number: Divide the numerator by the denominator and retain the remainder as the fraction (e.g., 5/2 = 2 1/2)
Operations with Fractions
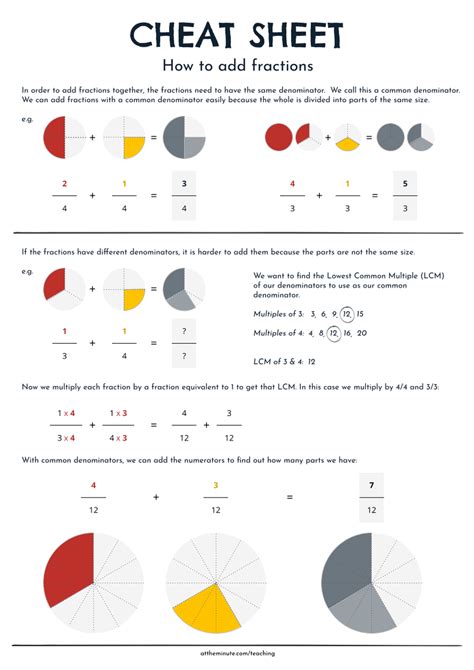
- Adding and Subtracting: Find a common denominator and add or subtract the numerators (e.g., 1/2 + 1/4 = 3/4)
- Multiplying: Multiply the numerators and denominators (e.g., 1/2 x 3/4 = 3/8)
- Dividing: Invert the second fraction and multiply (e.g., 1/2 ÷ 3/4 = 1/2 x 4/3 = 2/3)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Forgetting the units of fractions (e.g., 1/2 cup)
- Not simplifying fractions (e.g., using 6/12 instead of 1/2)
- Using the same denominator when subtracting fractions (e.g., 1/2 – 1/3 = 0/6)
Benefits of Understanding Fractions
Mastering fractions is crucial for:
- Real-World Applications: Measuring ingredients, calculating percentages, understanding ratios
- Science and Mathematics: Geometry, physics, algebra, statistics
- Financial Literacy: Interest rates, mortgages, investments
Pain Points Resolved
- Converting between fractions, decimals, and percentages: This cheat sheet provides clear conversion formulas.
- Simplifying and operating with fractions: Step-by-step instructions and examples overcome common hurdles.
- Understanding fractions in real-world contexts: Practical examples illustrate the importance of fractions in everyday life.
Applications Beyond Calculation
Fractomation: The use of fractions to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and solve problems in various fields such as manufacturing, engineering, and finance.
Tables for Quick Reference
| Fraction Type | Numerator | Denominator |
|---|---|---|
| Proper | Smaller than the denominator | |
| Improper | Greater than or equal to the denominator | |
| Mixed Number | Whole number with a proper fraction |
| Operation | Rule |
|---|---|
| Addition/Subtraction | Find common denominator |
| Multiplication | Multiply numerators and denominators |
| Division | Invert second fraction and multiply |
| Conversion | Formula |
|---|---|
| Decimal | Numerator ÷ Denominator |
| Percentage | Fraction x 100 |
| Mixed Number | Numerator ÷ Denominator (remainder as fraction) |
Conclusion
With this comprehensive fractions cheat sheet at your fingertips, you are well-equipped to conquer the world of fractions with confidence. Remember, practice makes perfect, so embrace the challenges and enjoy the satisfaction that comes with mastering this essential mathematical concept.