Why 87 to c Matters
Converting degrees Fahrenheit to degrees Celsius is a crucial skill in various fields, including science, engineering, meteorology, and everyday life. Understanding the conversion process ensures accurate temperature measurements, precise scientific calculations, and informed decision-making in different applications.

Benefits of 87 to c Conversion
- Improved Scientific Accuracy: Accurate temperature data is essential in scientific experiments, medical procedures, and industrial processes. Converting temperatures to Celsius, the scientific standard, enhances data reliability and comparability.
- Enhanced Weather Interpretation: Weather forecasts use degrees Celsius worldwide. Understanding 87 to c conversion allows individuals to interpret weather reports more effectively, plan outdoor activities, and make informed decisions based on temperature predictions.
- Simplified Cooking and Baking: Many recipes specify temperatures in degrees Celsius. Converting Fahrenheit measurements to Celsius ensures precise temperature control during cooking and baking, resulting in consistent and delicious results.
- International Communication: Celsius is the preferred temperature unit in most countries. Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius facilitates international collaborations, data exchange, and scientific communication.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
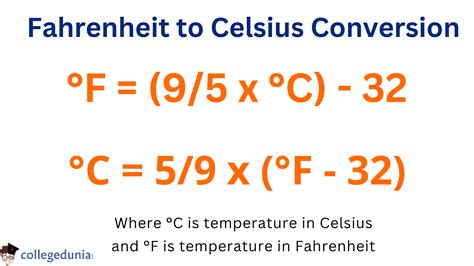
- Mixing Up Conversion Formulas: The formula for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius differs from Celsius to Fahrenheit. Remember, F = (C x 1.8) + 32, and C = (F – 32) / 1.8.
- Using Incorrect Coefficients: The conversion coefficients (1.8 and 32) are specific to the Fahrenheit-to-Celsius conversion. Do not substitute other values in the formula.
- Rounding Errors: Convert temperatures with the appropriate precision. Rounding errors can accumulate and lead to inaccurate measurements.
Innovative Applications of 87 to c Conversion
Thermosynthesis: Combining 87 to c conversion with advanced materials science could unlock novel applications in thermosynthesis. By precisely controlling temperatures in chemical reactions, researchers can synthesize new materials with tailored properties.
Personalized Cooling: Wearable devices incorporating 87 to c conversion can monitor body temperature and adjust cooling mechanisms accordingly. This technology could improve thermal comfort and reduce heat-related discomfort in various environments.
Thermophotovoltaics: By converting waste heat from industrial processes to electricity using thermophotovoltaics, 87 to c conversion can contribute to energy efficiency and renewable energy generation.
87 to c Conversion Tables
Table 1: Common Temperature Conversions
| Fahrenheit | Celsius |
|---|---|
| 32 | 0 |
| 68 | 20 |
| 86 | 30 |
| 104 | 40 |
| 122 | 50 |
Table 2: Cooking Temperature Conversions
| Fahrenheit | Celsius |
|---|---|
| 175 | 80 |
| 350 | 177 |
| 375 | 191 |
| 400 | 204 |
Table 3: Weather Temperature Conversions
| Fahrenheit | Celsius |
|---|---|
| 32 | 0 |
| 59 | 15 |
| 86 | 30 |
| 104 | 40 |
Table 4: Industrial Temperature Conversions
| Fahrenheit | Celsius |
|---|---|
| 212 | 100 |
| 392 | 200 |
| 662 | 350 |
| 1022 | 550 |
Conclusion
87 to c conversion is a fundamental skill with far-reaching applications. By understanding the conversion process, you can ensure accurate data, enhance scientific investigations, make informed decisions, and embrace innovative technologies. The tables provided in this article offer quick reference for common temperature conversions in various fields. By embracing 87 to c conversion, you empower yourself with precise temperature measurements and open the door to a world of possibilities.