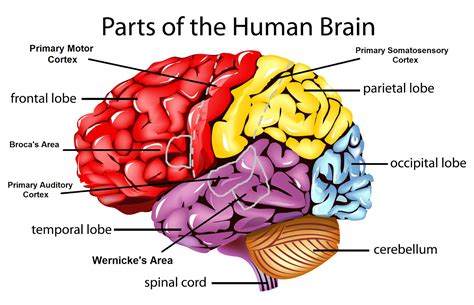
In the realm of AP Psychology, understanding the intricate workings of the brain is paramount to unraveling the complexities of human behavior. This comprehensive guide provides an exhaustive list of the brain’s key components and their crucial functions, empowering you to delve deeper into the fascinating world of neuroscience.

Forebrain: The Control Center
-
Frontal Lobe:
- Executive function, decision-making, planning
- Language production (Broca’s area)
- Working memory, attention
- Personality, social behavior
-
Parietal Lobe:
- Somatosensory perception (touch, pressure, temperature)
- Spatial processing, navigation
- Number and mathematical cognition
-
Temporal Lobe:
- Auditory perception (primary auditory cortex)
- Memory formation, retrieval (hippocampus)
- Language comprehension (Wernicke’s area)
-
Occipital Lobe:
- Primary visual cortex (processes visual input)
- Object recognition, color perception
Midbrain: The Relay Station
-
Thalamus:
- Sensory processing and relay
- Motor control
- Consciousness
-
Substantia Nigra:
- Motor control
- Parkinson’s disease
-
Red Nucleus:
- Coordination of movements
Hindbrain: The Survival System
-
Medulla Oblongata:
- Controls vital functions (breathing, heart rate, blood pressure)
- Reflexive movements (e.g., swallowing)
-
Pons:
- Relays sensory and motor information
- Helps maintain consciousness
-
Cerebellum:
- Coordinates movement, balance, equilibrium
Limbic System: The Emotional Center
-
Amygdala:
- Fear conditioning, emotional processing
- Stress response
-
Hippocampus:
- Memory formation, retrieval
-
Hypothalamus:
- Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep
- Hormone production
Subcortical Structures: Hidden Treasures
-
Basal Ganglia:
- Motor control, coordination
- Parkinson’s disease
-
Thalamus:
- Sensory processing and relay
- Consciousness
-
Hypothalamus:
- Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep
- Hormone production
-
Pituitary Gland:
- Secretes hormones that control growth, metabolism, blood pressure
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing the frontal lobe with the temporal lobe.
- Forgetting the key role of the hippocampus in memory formation.
- Underestimating the importance of the cerebellum in movement coordination.
How to Use This Guide Effectively
- Study the list of brain parts and their functions thoroughly.
- Create flashcards or notes for quick review and recall.
- Apply your knowledge to AP Psychology questions and practice tests.
- Seek additional resources (e.g., textbooks, online articles) for further understanding.
Why Understanding Brain Parts Matters
- Cognitive Function: Delving into the brain’s anatomy enhances our comprehension of cognitive processes like learning, memory, and attention.
- Psychological Disorders: Understanding the brain’s role in mental health disorders allows for more effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Neuroscientific Research: Knowledge of brain parts is crucial for advancing neuroscience research and developing interventions to address neurological conditions.
Benefits of Understanding Brain Parts
- Improved AP Psychology exam performance.
- Enhanced understanding of cognitive processes.
- Increased knowledge of mental health disorders and their treatments.
- Contribution to neuroscientific advancements.
Glossary of Terms
- Neuroanatomy: The study of the brain’s structure.
- Cognition: Mental processes involved in acquiring, storing, and using knowledge.
- Limbic System: A complex network of brain structures involved in emotion, memory, and motivation.
- Subcortical Structures: Brain structures located below the cortex.
Conclusion
Comprehending the complex network of brain parts and their functions is a fundamental aspect of AP Psychology. By leveraging this comprehensive guide, you can expand your knowledge of neuroscience, enhance your understanding of cognitive processes, and prepare for success in both the classroom and on the exam. Remember, the brain is a remarkable organ that holds the key to unlocking the mysteries of the human mind.