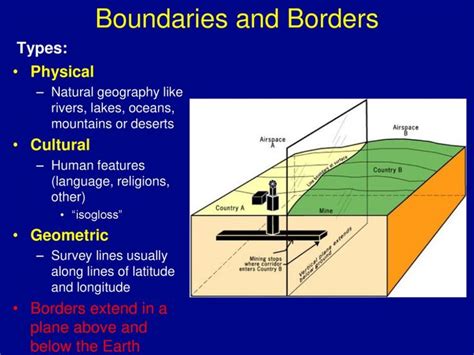
Understanding Geometric Boundaries
In AP Human Geography, geometric boundaries are lines or areas that separate regions or territories. They can be defined by physical features such as rivers, mountains, or deserts, or by political factors such as treaties or laws. Understanding geometric boundaries is crucial for comprehending the distribution of human populations, economic activities, and political systems around the world.

Types of Geometric Boundaries
There are several types of geometric boundaries commonly encountered in AP Human Geography:
- Natural Boundaries: These boundaries are formed by natural features of the landscape, such as rivers, mountains, or deserts. They can serve as both physical and psychological barriers to human movement and interaction.
- Political Boundaries: These boundaries are established by governments and divide regions into administrative units, such as countries, states, or provinces. They are often based on historical, cultural, or economic considerations.
- Cultural Boundaries: These boundaries mark the transition between different cultural regions. They can be based on language, religion, ethnicity, or other cultural factors.
- Economic Boundaries: These boundaries delineate areas with different economic characteristics, such as income levels, employment rates, or industrial development. They can influence the movement of people and resources.
Significance of Geometric Boundaries
Geometric boundaries have profound implications for human geography:
- Population Distribution: They impact the distribution of human populations, with people often concentrated near or along boundaries due to factors such as access to resources or trade routes.
- Economic Activities: Boundaries can affect the flow of goods and services, influencing trade patterns and economic development.
- Political Systems: Boundaries can shape political landscapes, defining the scope of government authority and territorial jurisdiction.
- Cultural Identity: Boundaries can contribute to cultural diversity and identity, as they often demarcate areas with distinct languages, customs, and traditions.
Applying Geometric Boundary Concepts
Geometric boundary concepts can be applied in various fields to solve real-world problems:
- Urban Planning: Boundaries can guide the development of cities and towns, ensuring balanced growth and access to resources.
- Natural Resource Management: Understanding boundaries can help protect natural resources and prevent conflicts over their use.
- Border Security: Boundaries are essential for managing international borders, preventing illegal immigration and transnational crime.
- Conflict Resolution: Boundaries can serve as a framework for resolving territorial disputes and promoting peace and stability.
Tables for Geometric Boundary Analysis
The following tables provide useful data for analyzing geometric boundaries:
| Type of Boundary | Examples | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Boundaries | Rivers, mountains, deserts | Physical barriers, transportation routes, population distribution |
| Political Boundaries | Country borders, state lines | Political authority, economic interactions, cultural differences |
| Cultural Boundaries | Language zones, religious regions | Identity formation, communication barriers, cultural exchange |
| Economic Boundaries | Economic development zones, trade regions | Resource allocation, job creation, investment attraction |
Strategies for Effective Boundary Management
Effective boundary management strategies include:
- Delimitation: Establishing clear and well-defined boundaries through negotiation and consensus.
- Demarcation: Physically marking boundaries on the ground using markers, fences, or other means.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitoring boundaries to ensure their integrity and prevent encroachment.
- Enforcement: Enforcing boundary regulations to prevent illegal crossings or other violations.
- Cooperation: Collaborating with neighboring regions to resolve boundary disputes and manage shared resources.
Conclusion
Geometric boundaries are fundamental concepts in AP Human Geography, shaping human interactions, economic activities, and political systems. Understanding the different types and significance of boundaries is crucial for comprehending the complexities of human geography and developing solutions to real-world problems. By applying geometric boundary concepts effectively, researchers, policymakers, and planners can contribute to a more just and equitable global community.