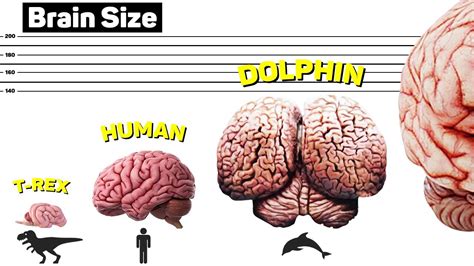
The average size of a human brain varies depending on age, gender, and other factors. However, the average adult human brain weighs approximately 1,300 to 1,400 grams (2.87 to 3.09 pounds).

Factors Affecting Brain Size
- Age: The brain grows rapidly during the early years of life, reaching its maximum size by the early 20s.
- Gender: On average, men have slightly larger brains than women.
- Genetics: Brain size is influenced by genetics, but the exact mechanisms are not fully understood.
- Environment: Certain environmental factors, such as nutrition and exposure to toxins, can affect brain size.
Variations in Brain Size
The size of the brain does not necessarily correlate with intelligence or overall cognitive function. In fact, some studies have shown that people with smaller brains may have higher IQ scores.
Average Size of Other Human Organs
In addition to the brain, here are the average sizes of other human organs:
| Organ | Average Size |
|---|---|
| Heart | 250-300 grams (8.82-10.58 ounces) |
| Liver | 1,500 grams (3.31 pounds) |
| Kidneys | 150 grams (5.29 ounces) each |
| Stomach | 1,000 grams (2.2 pounds) |
| Pancreas | 70 grams (2.47 ounces) |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Assuming that brain size is an indicator of intelligence: Brain size does not always correlate with intelligence.
- Overestimating the size of the human brain: The human brain is relatively small compared to the brains of other animals.
- Underestimating the complexity of the brain: The brain is an incredibly complex organ with billions of neurons and trillions of connections.
How to Measure Brain Size
Brain size can be measured using various methods, including:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This technique uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: This technique uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain.
- Ultrasonography: This technique uses sound waves to create images of the brain.
Why Brain Size Matters
Brain size is important for several reasons:
- Cognitive function: The brain is responsible for all cognitive functions, including learning, memory, and decision-making.
- Motor function: The brain controls movement and coordination.
- Sensory perception: The brain receives and processes sensory information from the environment.
- Emotional regulation: The brain regulates emotions and behavior.
Benefits of a Healthy Brain
Maintaining a healthy brain is essential for overall well-being. Here are some benefits of a healthy brain:
- Improved cognitive function: A healthy brain allows for better learning, memory, and problem-solving abilities.
- Reduced risk of neurological disorders: A healthy brain is less likely to develop diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Improved mood and well-being: A healthy brain helps regulate emotions and promotes a positive outlook on life.
- Increased life expectancy: A healthy brain is associated with longer life expectancy.
Conclusion
The average size of a human brain varies depending on several factors. However, regardless of size, the brain is an incredibly complex and vital organ that plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being.