Introduction

In the ever-evolving digital landscape, protecting sensitive information has become paramount. The principles of information security serve as the foundation for safeguarding data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. These principles guide organizations in establishing robust security systems and practices to mitigate threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical assets.
Core Principles of Information Security
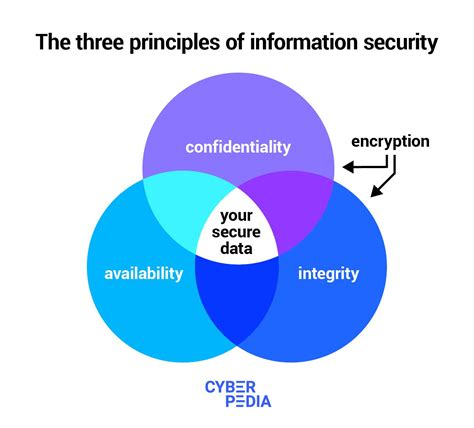
- Confidentiality: Ensures that information is accessible only to authorized individuals or entities.
- Integrity: Preserves the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of information.
- Availability: Guarantees that information is accessible when needed by authorized users.
Whitman’s Principles of Information Security
Professor Michael Whitman, an esteemed expert in cybersecurity, has developed a comprehensive framework of principles that expand on the traditional CIA triad. These principles provide a holistic approach to information security, emphasizing risk management, governance, compliance, ethics, and education.
Whitman’s Expanded Principles
- Risk Management: Identifies, assesses, and mitigates potential risks to information assets.
- Governance: Establishes clear roles, responsibilities, and policies for managing information security.
- Compliance: Adheres to legal, regulatory, and industry-specific requirements for data protection.
- Ethics: Promotes ethical behavior in the use of information systems and technologies.
- Education: Provides training and awareness programs to enhance information security knowledge and practices.
Benefits of Adhering to Information Security Principles
Organizations that embrace these principles benefit from:
- Reduced risk of data breaches and cyberattacks
- Enhanced protection of sensitive and confidential information
- Improved compliance with regulatory mandates
- Increased trust and credibility with stakeholders
- Competitive advantage in the digital market
Key Statistics
- According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 is $4.35 million.
- The World Economic Forum estimates that cybercrime will cost businesses $6 trillion annually by 2025.
- A study by Verizon found that 85% of data breaches involve human error.
Innovative Applications of Information Security Principles
These principles can inspire novel applications to enhance data security:
- Cybersecurity Mesh: A decentralized security architecture that distributes security controls across multiple locations.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): An approach that grants access to resources only after verifying and authenticating each request.
- Data Anonymization: The process of removing personally identifiable information (PII) from data to protect privacy.
Tables
| Security Principle | Definition |
|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Limiting access to authorized individuals |
| Integrity | Preserving accuracy and consistency of information |
| Availability | Ensuring accessibility when needed |
| Risk Management | Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks |
| Governance | Establishing clear roles and responsibilities |
| Compliance | Adhering to legal and regulatory requirements |
| Ethics | Promoting ethical behavior in information systems |
| Education | Providing training and awareness programs |
Tips and Tricks
- Implement multi-factor authentication for enhanced security.
- Regularly update software and security patches to address vulnerabilities.
- Conduct security awareness training for all employees.
- Establish clear incident response plans to manage security breaches effectively.
- Encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What are the key differences between confidentiality, integrity, and availability?
– Confidentiality ensures data is only accessed by authorized users.
– Integrity preserves its accuracy and consistency.
– Availability guarantees accessibility when needed. -
Why is risk management important in information security?
– It identifies potential threats, assesses their likelihood and impact, and develops mitigation strategies. -
How can I improve my personal information security?
– Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication.
– Be cautious of suspicious emails and websites.
– Keep software and apps updated regularly. -
What are some common threats to information security?
– Malware, phishing attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access. -
What is the role of encryption in information security?
– Encryption converts data into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access. -
How can I stay informed about the latest information security trends?
– Attend conferences, subscribe to industry publications, and engage with cybersecurity professionals online.
Conclusion
Adhering to the principles of information security is crucial for protecting sensitive data and mitigating cyber threats. By implementing Whitman’s expanded framework, organizations can establish comprehensive security programs that enhance confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Continuously educating employees, embracing innovative technologies, and staying up-to-date with the latest threats are essential to safeguard information assets in the dynamic digital landscape.