Navigating the Path to Medical School

The journey to becoming a physician begins with selecting the right undergraduate major. The path to medical school requires a strong foundation in the sciences, but the choice of major can significantly influence your chances of acceptance. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the best majors for premed students, highlighting their benefits, key requirements, and common mistakes to avoid.
The Essential Elements of a Premed Major
Regardless of your specific major, pursuing a premed track requires fulfilling core course requirements in:
- Biology
- Chemistry (including organic and biochemistry)
- Physics
- Mathematics
Benefits of a Science-Focused Major
Majoring in a science field offers several advantages for premed students:
- Solid Academic Foundation: A science major provides a comprehensive understanding of the natural sciences, which are essential for understanding medical concepts.
- Preparation for MCAT: The MCAT (Medical College Admission Test) heavily emphasizes science subjects, and a science major ensures adequate preparation.
- Research Opportunities: Science majors often provide ample opportunities for undergraduate research, which is highly valued by medical schools.
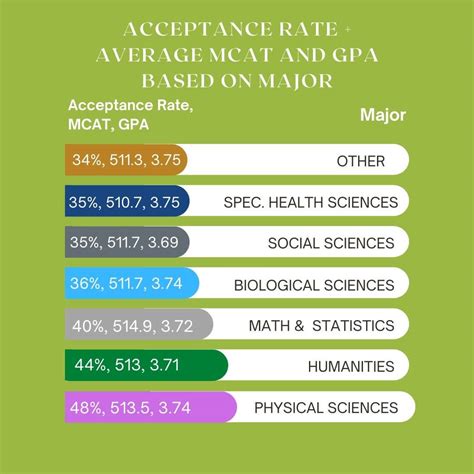
Top Majors for Premed
Based on data from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), the following majors are among the most popular and successful pathways for premed students:
Biology
Key Requirements:
- General Biology
- Cell and Molecular Biology
- Genetics
- Physiology
Benefits:
- Broad exposure to foundational biological concepts
- Strong preparation for medical school coursework
- Opportunities for diverse research experiences
Chemistry
Key Requirements:
- General Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
Benefits:
- In-depth understanding of chemical principles
- Preparation for MCAT and medical school curriculum
- Career opportunities in chemistry and related fields
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Key Requirements:
- Biochemistry
- Molecular Biology
- Cell Biology
- Genetics
Benefits:
- Specialized knowledge of biological processes at the molecular level
- Preparation for research careers in biomedicine
- Applicability to medical fields such as genetics and biotechnology
Neuroscience
Key Requirements:
- Neuroanatomy
- Neurophysiology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Developmental Neuroscience
Benefits:
- Understanding of the nervous system’s structure and function
- Preparation for medical specialties in neurology and psychiatry
- Growing field with diverse career opportunities
Psychology
Key Requirements:
- General Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Abnormal Psychology
- Physiological Psychology
Benefits:
- Insight into human behavior and mental processes
- Understanding of the psychological aspects of medicine
- Preparation for careers in psychiatry and counseling
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Neglecting Non-Science Courses: While science majors are essential, it’s crucial to also excel in humanities, social sciences, and writing to develop well-rounded knowledge.
- Overloading with Advanced Courses: While challenging yourself academically is important, taking too many advanced courses can lead to burnout and decreased performance.
- Ignoring Extracurricular Activities: Involvement in clubs, research, and volunteer work demonstrates commitment and leadership qualities.
- Underestimating the MCAT: The MCAT is a challenging exam that requires thorough preparation and practice. Start studying early.
- Not Seeking Faculty Mentorship: Faculty mentors can provide guidance, support, and opportunities for research and career development.
Why Major Matters
Your major not only affects your academic preparation but also has long-term implications:
- Career Options: A science major provides a foundation for a wide range of careers in healthcare, academia, and research.
- Medical School Admissions: Medical schools consider both your GPA and your major when making admissions decisions. A strong science major can significantly improve your chances.
- Personal Growth: Pursuing a science major fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills that are essential for a successful career in medicine.
Benefits of a Premed Major
- Access to Specialized Knowledge: Premed majors provide a deep understanding of the human body and medical practices.
- Preparation for Medical School: Core science courses and research opportunities prepare students for the rigors of medical school.
- Career Opportunities: A science major qualifies students for various healthcare professions, including medicine, dentistry, and nursing.
- Intellectual Stimulation: Studying science fosters curiosity, critical thinking, and a passion for learning.
- Social Responsibility: A science-based education empowers individuals to contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge and improve the well-being of others.
FAQs
1. Is it possible to get into medical school without a science major?
While it is possible, it is less common. Medical schools generally prefer applicants with a strong science background.
2. What is the average GPA required for medical school?
The average GPA of accepted medical school applicants is around 3.7. However, this can vary depending on the school and other factors.
3. What are the most important factors for medical school admissions?
GPA, MCAT score, extracurricular activities, and research experience are all highly considered.
4. How can I prepare for the MCAT?
Official preparation materials, practice questions, and full-length tests are essential for success on the MCAT.
5. What are the best resources for premed students?
The AAMC, college advisors, and online forums provide valuable advice and resources.
6. What are some career options for science majors besides medicine?
Science majors can pursue careers in research, academia, healthcare administration, and various industries.
7. How can I make the most of my undergraduate experience as a premed?
Seek out research opportunities, engage in extracurricular activities, maintain a high GPA, and connect with faculty mentors.
8. What are some common challenges faced by premed students?
Rigorous coursework, balancing academic and extracurricular commitments, and the pressure of medical school admissions can be challenging.