Introduction

Visual perception, the ability to interpret and comprehend the world around us, is a complex cognitive process. Feature detectors, specialized neurons in the visual cortex, play a crucial role in this process by extracting specific visual cues from our environment.
What are Feature Detectors?
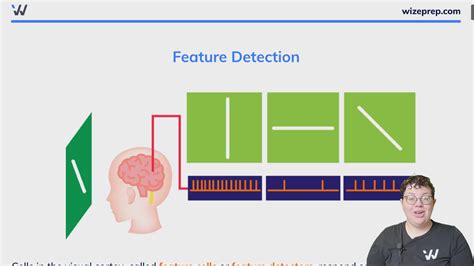
Feature detectors are neurons that respond selectively to specific visual features, such as edges, corners, or colors. They are organized hierarchically, with lower-level detectors responding to simple features and higher-level detectors responding to more complex ones.
How Feature Detectors Work
When light enters the eye, it is converted into electrical signals that travel along the optic nerve to the visual cortex. Feature detectors in the visual cortex compare these signals to stored representations of visual features. If a match is found, the feature detector fires, indicating the presence of that feature in the visual field.
Types of Feature Detectors
There are many types of feature detectors, each tuned to a specific visual cue. Some common types include:
- Edge detectors: Respond to sharp changes in brightness across a line.
- Corner detectors: Detect the presence of corners or angles.
- Motion detectors: Respond to movement in the visual field.
- Color detectors: Respond to specific wavelengths of light.
Role in Visual Perception
Feature detectors play a critical role in visual perception by extracting important visual cues from the environment. These cues are then used to:
- Identify objects
- Recognize faces
- Navigate the world
- Perceive depth and motion
Research and Applications
Extensive research has been conducted on feature detectors, providing valuable insights into visual perception and cognitive processes. Applications of feature detection include:
- Object detection: Identifying objects in images for computer vision tasks.
- Medical imaging: Detecting anomalies or diseases in medical scans.
- Robotics: Enabling robots to navigate and interact with their surroundings.
Table 1: Types of Feature Detectors
| Type | Visual Cue |
|---|---|
| Edge detector | Sharp changes in brightness |
| Corner detector | Corners or angles |
| Motion detector | Movement |
| Color detector | Specific wavelengths of light |
Table 2: Role of Feature Detectors in Visual Perception
| Task | Feature Detectors |
|---|---|
| Object identification | Edge, corner, and color detectors |
| Face recognition | Feature detectors tuned to facial features |
| Navigation | Motion and edge detectors |
| Depth perception | Binocular disparity and motion parallax detectors |
Table 3: Effective Strategies for Enhancing Feature Detection
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Contrast enhancement | Adjust image brightness and contrast to improve feature visibility |
| Histogram equalization | Distribute image pixel values evenly to enhance contrast |
| Edge sharpening | Apply filters to highlight edges in images |
| Feature extraction algorithms | Use computational algorithms to extract specific features from images |
Table 4: Benefits of Feature Detection
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved image analysis | Enables more accurate and efficient extraction of visual information |
| Enhanced object recognition | Supports object recognition systems in complex environments |
| Increased environmental awareness | Provides a basis for robotics and autonomous navigation |
| Advanced medical imaging | Facilitates early disease detection and improved treatment planning |
Conclusion
Feature detectors are a fundamental component of visual perception, enabling us to extract meaningful information from our environment. Their role in image analysis, object recognition, and other cognitive processes has made them indispensable to computer vision, robotics, and other fields. As research continues to explore the mechanisms and applications of feature detectors, we can expect even more advancements in our understanding of vision and the development of new technologies that enhance our interactions with the world.