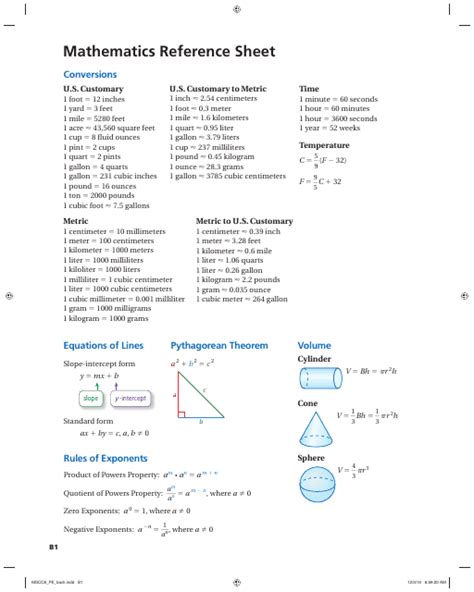
Introduction
The world of mathematics is vast and ever-evolving, with a plethora of formulas and equations that guide our understanding of various phenomena. From simple arithmetic to complex calculus and beyond, mathematical formulas play a pivotal role in solving real-world problems, advancing scientific research, and enabling technological breakthroughs.

This comprehensive mathematical formula sheet serves as an invaluable resource for students, educators, and professionals alike. It encompasses a wide range of formulas covering key mathematical concepts, from basic algebra to advanced calculus. By providing quick access to essential formulas, this sheet helps streamline problem-solving, enhance comprehension, and foster a deeper understanding of mathematical principles.
Algebra
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Slope-intercept form of a linear equation: y = mx + b
- Point-slope form of a linear equation: y – y1 = m(x – x1)
- Two-point form of a linear equation: y – y1 / x – x1 = y2 – y1 / x2 – x1
- Standard form of a linear inequality: Ax + By ≤/≥ C
Quadratic Equations
- Quadratic formula: ax² + bx + c = 0, x = (-b ± √(b² – 4ac)) / 2a
- Completing the square: ax² + bx + c = (ax² + bx + b²/4a) + c – b²/4a = ((2ax + b)/2a)² + c – b²/4a
- Factoring: ax² + bx + c = (px + q)(rx + s), where p, q, r, and s are constants
Polynomials
- Factor theorem: If p(x) is a polynomial of degree n, then (x – a) is a factor of p(x) if and only if p(a) = 0
- Remainder theorem: If p(x) is a polynomial of degree n, then the remainder when p(x) is divided by (x – a) is p(a)
Trigonometry
Trigonometric Identities
- Sine: sin(θ) = opposite / hypotenuse
- Cosine: cos(θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse
- Tangent: tan(θ) = opposite / adjacent
- Pythagorean identity: sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1
Angles and Radians
- One radian = 180 / π degrees
- One degree = π / 180 radians
- Conversion between degrees and radians: θ (radians) = θ (degrees) * π / 180
Special Angles
- sin(0°) = 0, cos(0°) = 1, tan(0°) = 0
- sin(30°) = 1/2, cos(30°) = √3 / 2, tan(30°) = √3 / 3
- sin(45°) = cos(45°) = √2 / 2, tan(45°) = 1
Calculus
Limits and Continuity
- Limit of a function: limx→a f(x) = L, if for every ε > 0, there exists a δ > 0 such that whenever |x – a| < δ, then |f(x) - L| < ε
- Continuity of a function: A function f(x) is continuous at x = a if limx→a f(x) = f(a)
Differentiation
- Derivative of a function: f'(x) = limh→0 (f(x + h) – f(x)) / h
-
Rules of differentiation:
-
Power rule: d(x^n) / dx = nx^(n-1)
- Sum/difference rule: d(f(x) ± g(x)) / dx = f'(x) ± g'(x)
- Product rule: d(f(x)g(x)) / dx = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x)
- Quotient rule: d(f(x) / g(x)) / dx = (g(x)f'(x) – f(x)g'(x)) / g²(x)
Integration
- Integral of a function: ∫ f(x) dx
- Fundamental theorem of calculus: ∫ a^b f(x) dx = F(b) – F(a), where F(x) is an antiderivative of f(x)
Matrix Algebra
Matrix Operations
- Matrix addition: [a11 a12 … a1n] + [b11 b12 … b1n] = [a11+b11 a12+b12 … a1n+b1n]
- Matrix multiplication: [a11 a12 … a1n] * [b11 b12 … bmn] = [a11b11 + a12b21 + … + a1nbn1 a11b12 + a12b22 + … + a1nbn2 … a11b1m + a12b2m + … + a1n*bnm]
- Matrix determinant: det([a11 a12 … a1n]) = a11C11 – a12C12 + … + a1n*C1n, where Cij is the cofactor of aij
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
- Eigenvalue of a matrix: λ is an eigenvalue of A if there exists a non-zero vector x such that Ax = λx
- Eigenvector of a matrix: x is an eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue λ if Ax = λx
Statistics and Probability
Descriptive Statistics
- Mean: μ = (1/n) Σxi
- Variance: σ² = (1/n) Σ(xi – μ)²
- Standard deviation: σ = √(σ²)
Probability Distributions
- Normal distribution: f(x) = (1 / (σ√(2π))) * e^(-(x-μ)² / (2σ²))
- Binomial distribution: P(X = k) = n! / k!(n-k)! * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k)
- Poisson distribution: P(X = k) = (λ^k * e^(-λ)) / k!
Tables for Quick Reference
Table 1: Trigonometric Identities
| Identity | Formula |
|---|---|
| Pythagorean | sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1 |
| Double-angle | sin(2θ) = 2sin(θ)cos(θ) |
| Half-angle | sin(θ/2) = ±√((1 – cos(θ)) / 2) |
| Sum-to-product | sin(θ + φ) = sin(θ)cos(φ) + cos(θ)sin(φ) |
| Product-to-sum | sin(θ)cos(φ) = (1/2)(sin(θ + φ) + sin(θ – φ)) |
Table 2: Matrix Properties
| Property | Formula |
|---|---|
| Associative | A(BC) = (AB)C |
| Distributive | A(B + C) = AB + AC |
| Identity | AI = IA = A |
| Inverse | A⁻¹A = AA⁻¹ = I |
| Transpose | (Aᵀ)ᵀ = A |
Table 3: Calculus Rules
| Rule | Formula |
|---|---|
| Power rule | d(x^n) / dx = nx^(n-1) |
| Sum/difference rule | d(f(x) ± g(x)) / dx = f'(x) ± g'(x) |
| Chain rule | d(f(g(x))) / dx = f'(g(x))g'(x) |
| Product rule | d(f(x)g(x)) / dx = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x) |
| Quotient rule | d(f(x) / g(x)) / dx = (g(x)f'(x) – f(x)g'(x)) / g²(x) |
Table 4: Statistical Distributions
| Distribution | Probability Density Function |
|---|---|
| Normal | f(x) = (1 / (σ√(2π))) * e^(-(x-μ)² / (2σ²)) |
| Binomial | P(X = k) = n! / k!(n-k)! * p^k * (1-p)^(n-k) |
| Poisson | P(X = k) = (λ^k * e^(-λ)) / k! |
Tips and Tricks for Efficient Formula Utilization
- Memorize frequently used formulas: Identify the essential formulas that you encounter regularly and make an effort to commit them to memory.
- Understand the underlying principles: Don’t just memorize formulas; try to comprehend the mathematical concepts and relationships that they represent.
- Use a calculator judiciously: While calculators are convenient,