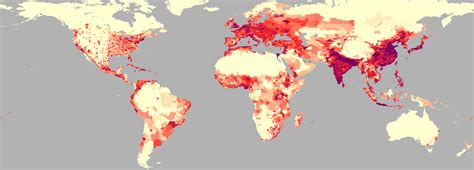
Introduction
Population distribution refers to the spatial arrangement of people across the Earth’s surface. It encompasses the study of how population is distributed across different regions, cities, and rural areas, and the factors that influence these patterns. Understanding population distribution is crucial for various fields, including urban planning, public health, environmental management, and economic development.

Key Concepts
1. Absolute and Relative Density
– Absolute density: Refers to the number of people per unit area, typically measured in persons per square kilometer or mile.
– Relative density: Indicates the concentration of population relative to other areas or regions.
2. Population Patterns
– Clustered distribution: Occurs when people live in concentrated settlements, such as cities or urban areas.
– Dispersed distribution: Refers to a situation where people are spread out over a wide area, often in rural or sparsely populated regions.
– Linear distribution: Occurs when people reside along linear features like rivers, roads, or coastlines.
3. Factors Influencing Population Distribution
– Physical factors: Climate, landforms, natural resources, and availability of water.
– Economic factors: Employment opportunities, industrial development, and access to markets.
– Social factors: Cultural values, migration patterns, and social networks.
– Political factors: Boundaries, government policies, and conflicts.
Global Patterns of Population Distribution
1. Concentration in Urban Areas
– Over 55% of the world’s population lives in urban areas, a figure projected to rise to 68% by 2050.
– Urbanization is driven by economic opportunities, better access to education, and healthcare, and improved living conditions.
2. Regional Disparities
– The distribution of population is uneven across the globe. Asia and Europe are the most populous continents, accounting for approximately 60% of the world’s population.
– Developed countries tend to have lower population densities than developing countries.
3. Coastal Concentration
– Approximately 40% of the world’s population lives within 100 kilometers of the coast.
– Coastal areas offer access to transportation, trade, and fishing resources.
Consequences of Population Distribution
1. Urban Challenges
– Overcrowding, pollution, inadequate housing, and strain on infrastructure are common challenges in densely populated urban areas.
2. Rural Decline
– Rural areas may experience population loss due to migration to urban centers, resulting in social, economic, and environmental problems.
3. Resource Scarcity
– Uneven population distribution can lead to resource scarcity in certain regions, particularly in areas with limited water, land, and other resources.
Applications of Population Distribution Analysis
1. Urban Planning
– Understanding population distribution patterns helps planners design cities, improve transportation systems, and provide adequate housing and services.
2. Public Health
– Mapping population distribution allows health officials to identify areas with higher needs for healthcare facilities, vaccination campaigns, and disease prevention programs.
3. Economic Development
– Analyzing population distribution can guide investments in infrastructure, industry, and job creation in regions with high population growth or declining populations.
4. Environmental Conservation
– Information on population distribution supports efforts to protect ecosystems and control pollution by identifying areas with high human impact or potential environmental risks.
Effective Strategies for Managing Population Distribution
1. Promote Sustainable Urbanization
– Invest in infrastructure, housing, and services in urban areas to accommodate population growth while minimizing negative consequences.
2. Encourage Rural Development
– Provide incentives for economic opportunities and improve living conditions in rural areas to prevent population loss.
3. Manage Migration
– Implement policies to regulate migration patterns, reduce regional disparities, and ensure orderly and sustainable population distribution.
Conclusion
Population distribution is a complex and dynamic concept that plays a vital role in various aspects of human society, environment, and development. Understanding the patterns, factors, and consequences of population distribution is essential for policymakers, planners, and researchers to address the challenges and opportunities associated with managing the spatial distribution of people on Earth. Through careful analysis and effective strategies, we can harness the benefits of population distribution while mitigating its potential negative impacts.