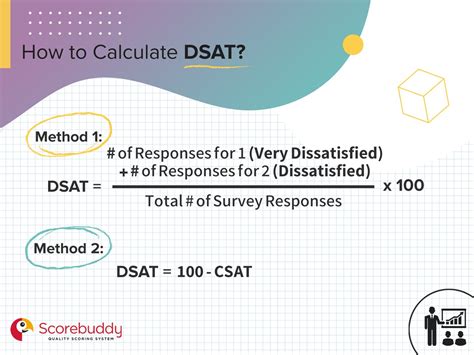
DSAT (Data Science Analytics Test) is a standardized exam that assesses the knowledge and skills of individuals in data science and analytics. It is designed to measure candidates’ proficiency in various aspects of data science, including data manipulation, data analysis, and data visualization.

Importance of DSAT
In today’s data-driven world, professionals with strong data science and analytics skills are in high demand. DSAT certification demonstrates an individual’s competency in this field and provides several benefits:
- Enhanced Job Opportunities: DSAT certification can open doors to a wide range of job opportunities in data science, analytics, and related fields.
- Improved Career Growth: By passing the DSAT exam, professionals can enhance their career prospects and advance to leadership roles in data-intensive industries.
- Increased Earning Potential: Certified data scientists and analysts typically earn higher salaries than their non-certified counterparts.
- Professional Recognition: DSAT certification is a recognized credential that signifies an individual’s expertise in data science and analytics.
DSAT Exam Structure and Syllabus
The DSAT exam consists of 100 multiple-choice questions covering the following five domains:
| Domain | Percentage of Exam | Key Concepts |
|---|---|---|
| Data Manipulation | 30% | Data cleaning, transformation, and wrangling |
| Data Analysis | 40% | Statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling |
| Data Visualization | 20% | Creating and interpreting data visualizations |
| Business Applications | 5% | Understanding data-driven decision-making |
| Ethics and Legal Considerations | 5% | Data privacy, ethical data use, and regulatory compliance |
Preparing for DSAT
Preparing for the DSAT exam requires a comprehensive understanding of data science and analytics concepts. Candidates can prepare by:
- Studying the official DSAT study guide: This guide provides detailed information about the exam structure, syllabus, and practice questions.
- Taking online courses or workshops: These courses offer structured learning in specific data science domains.
- Practicing with sample questions: Practicing with sample questions helps candidates familiarize themselves with the exam format and question types.
- Building a project portfolio: Creating a portfolio of personal data science projects demonstrates practical skills and can be valuable for interview preparation.
DSAT Scoring and Results
The DSAT exam is scored on a scale of 1 to 5, with a passing score of 3. Candidates who pass the exam receive a DSAT certification that is valid for three years.
Conclusion
DSAT certification is a valuable credential for individuals looking to advance their careers in data science and analytics. It demonstrates an individual’s knowledge and skills in this rapidly growing field and can lead to increased job opportunities, career growth, and higher earning potential. With a targeted preparation plan and a comprehensive understanding of the exam syllabus, candidates can increase their chances of success on the DSAT exam.
Additional Information
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Who should take the DSAT exam?
– Individuals with a background in data science, analytics, statistics, or a related field who want to validate their skills and advance their career. -
What are the prerequisites for taking the DSAT exam?
– A bachelor’s degree in a field related to data science, analytics, or a related field. -
How long does it take to prepare for the DSAT exam?
– Preparation time varies depending on an individual’s background and the amount of time they can commit to studying. Many candidates spend several months to a year preparing. -
What resources are available to help candidates prepare for the DSAT exam?
– Official study guide, online courses, workshops, and sample questions. -
How is the DSAT exam scored?
– The exam is scored on a scale of 1 to 5, with a passing score of 3. -
How long is the DSAT certification valid for?
– Three years.
Tables
Table 1: DSAT Exam Structure
| Domain | Percentage of Exam | Key Concepts |
|---|---|---|
| Data Manipulation | 30% | Data cleaning, transformation, and wrangling |
| Data Analysis | 40% | Statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling |
| Data Visualization | 20% | Creating and interpreting data visualizations |
| Business Applications | 5% | Understanding data-driven decision-making |
| Ethics and Legal Considerations | 5% | Data privacy, ethical data use, and regulatory compliance |
Table 2: DSAT Preparation Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Study the official study guide | Provides detailed information about the exam structure, syllabus, and practice questions. |
| Take online courses or workshops | Offers structured learning in specific data science domains. |
| Practice with sample questions | Familiarizes candidates with the exam format and question types. |
| Build a project portfolio | Demonstrates practical skills and can be valuable for interview preparation. |
Table 3: Benefits of DSAT Certification
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Job Opportunities | Opens doors to a wide range of job opportunities in data science, analytics, and related fields. |
| Improved Career Growth | Enhances career prospects and advances to leadership roles in data-intensive industries. |
| Increased Earning Potential | Certified data scientists and analysts typically earn higher salaries than their non-certified counterparts. |
| Professional Recognition | A recognized credential that signifies an individual’s expertise in data science and analytics. |
Table 4: Who Should Consider DSAT Certification?
| Individual | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Scientists | Professionals who work with data to solve business problems. |
| Data Analysts | Professionals who analyze data to extract insights and make recommendations. |
| Business Analysts | Professionals who use data to understand business requirements and develop solutions. |
| Statisticians | Professionals with a strong foundation in statistical analysis and modeling. |
| Researchers | Professionals who use data to conduct research and draw conclusions. |