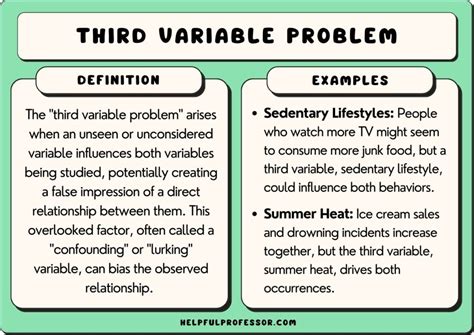
In statistics, the third variable problem refers to the phenomenon where a relationship between two variables is influenced by a third unobserved or unmeasured variable. This can lead to false conclusions about the relationship between the two original variables.

An Example of the Third Variable Problem
Consider the following example:
- Two variables:
- X: Number of hours spent studying
- Y: Grade on a test
- Positive relationship:
- Students who study more hours tend to get higher grades on tests
This relationship suggests that studying more hours leads to better grades. However, there may be a third variable that is influencing both the number of hours spent studying and the grade on the test.
- Third variable:
- Z: Student’s intelligence
Intelligent students are more likely to:
- Study more hours
- Get higher grades on tests
In this case, the third variable of student intelligence is influencing both the number of hours spent studying and the grade on the test. This can lead to a false conclusion that studying more hours leads to better grades, when in reality it is student intelligence that is causing both the increased study time and the higher grades.
How to Address the Third Variable Problem
The third variable problem can be addressed through a variety of methods, including:
- Randomized controlled trials: Assigning subjects to treatment and control groups randomly can help to control for the effects of third variables.
- Matching: Matching subjects on relevant characteristics can help to ensure that the treatment and control groups are similar in ways that could influence the results.
- Regression analysis: Regression analysis can be used to control for the effects of third variables by including them as independent variables in the model.
- Stratification: Stratifying the sample by third variables can help to ensure that the treatment and control groups are similar in ways that could influence the results.
Implications of the Third Variable Problem
The third variable problem can have significant implications for research and decision-making. It is important to be aware of the potential for third variables to influence the results of a study and to take steps to address this problem.
Conclusion
The third variable problem is a common challenge in research and decision-making. By understanding the concept of the third variable problem and using appropriate methods to address it, researchers and decision-makers can increase the validity and reliability of their conclusions.