Introduction

Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and energy in the form of sugar. It is a complex process that involves many different steps, and it is essential for life on Earth.
POGIL Answer Key
The following is a POGIL answer key for the topic of photosynthesis. This answer key is provided to help students check their understanding of the material and to identify any areas where they need additional support.
1. What is the overall equation for photosynthesis?
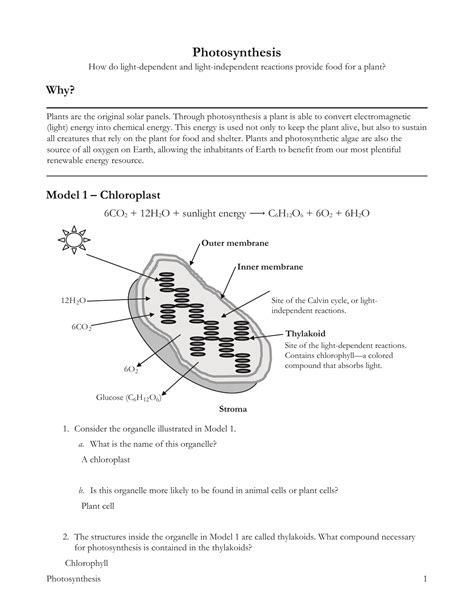
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
2. What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis?
Reactants:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Water (H2O)
- Light energy
Products:
- Glucose (C6H12O6)
- Oxygen (O2)
3. Where does photosynthesis take place?
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells. Chloroplasts are small, green organelles that contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light energy.
4. What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll absorbs light energy and uses it to power the chemical reactions of photosynthesis.
5. What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
- The light-dependent reactions
- The Calvin cycle
6. What happens during the light-dependent reactions?
During the light-dependent reactions, light energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen is used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH, and the oxygen is released as a waste product.
7. What happens during the Calvin cycle?
During the Calvin cycle, hydrogen from NADPH and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere are used to synthesize glucose.
8. What is the importance of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is essential for life on Earth. It provides the oxygen that we breathe and the food that we eat. It also helps to regulate the Earth’s climate by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Applications of Photosynthesis
The principles of photosynthesis have been used to develop a variety of applications, including:
- Biofuels: Photosynthesis can be used to produce biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel. Biofuels are renewable and sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels.
- Solar energy: Photosynthesis can be used to convert sunlight into electricity. Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of energy.
- Carbon capture and storage: Photosynthesis can be used to capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it underground. Carbon capture and storage is a technology that can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is a complex and essential process that is essential for life on Earth. The principles of photosynthesis have been used to develop a variety of applications that can help to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges, such as climate change and energy security.
Additional Resources
Table 1: The Reactants and Products of Photosynthesis
| Reactant | Product |
|---|---|
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | Glucose (C6H12O6) |
| Water (H2O) | Oxygen (O2) |
| Light energy |
Table 2: The Two Main Stages of Photosynthesis
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Light-dependent reactions | Light energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. |
| Calvin cycle | Hydrogen from NADPH and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere are used to synthesize glucose. |
Table 3: Applications of Photosynthesis
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Biofuels | Photosynthesis can be used to produce biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel. |
| Solar energy | Photosynthesis can be used to convert sunlight into electricity. |
| Carbon capture and storage | Photosynthesis can be used to capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it underground. |
Table 4: The Importance of Photosynthesis
| Importance | Description |
|---|---|
| Provides the oxygen that we breathe | Photosynthesis produces the oxygen that we breathe. |
| Provides the food that we eat | Photosynthesis produces the food that we eat. |
| Helps to regulate the Earth’s climate | Photosynthesis absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which helps to regulate the Earth’s climate. |