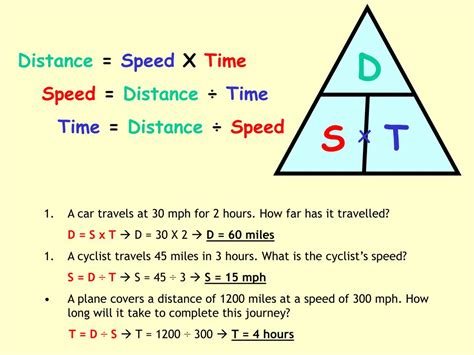
In the realm of human perception and response, the concept of the “4-second rule” holds significant relevance. This rule suggests that when an individual encounters an urgent stimulus within a distance of 4 seconds or less, they are more likely to react promptly and effectively.

Understanding the 4-Second Urgent Time and Distance
The 4-second rule is rooted in the intricate interplay between sensory perception, cognitive processing, and motor response. When a stimulus is detected, it triggers a series of neural impulses that travel from the sensory receptors to the brain. The brain then interprets the stimulus, evaluates its significance, and generates an appropriate response.
In situations where the stimulus is urgent and poses an immediate threat, the brain prioritizes the response process. It bypasses certain cognitive steps, such as conscious decision-making, and initiates an immediate motor response. This streamlined process allows individuals to react swiftly without losing valuable time.
Applications of the 4-Second Urgent Time and Distance
The 4-second urgent time and distance principle finds application in various fields, including:
- Traffic Safety: Drivers must react quickly and appropriately to unexpected hazards on the road, such as sudden braking or lane changes. The 4-second rule provides a reasonable time frame for drivers to assess the situation and initiate evasive maneuvers.
- Emergency Response: First responders, such as firefighters and paramedics, must act rapidly and decisively to mitigate emergencies. The 4-second rule highlights the importance of immediate response times in life-threatening situations.
- Sports and Athletics: Athletes rely on quick reaction times to gain a competitive edge. The 4-second rule underscores the critical role of anticipation and rapid decision-making in sports performance.
- Human-Computer Interaction: Designers of user interfaces and software applications strive to minimize response times and provide users with a seamless experience. The 4-second rule serves as a benchmark for acceptable response delays in interactive systems.
Factors Influencing the 4-Second Urgent Time and Distance
Several factors can influence the 4-second urgent time and distance, including:
- Age: As individuals age, their reaction times tend to slow down due to changes in cognitive and motor function.
- Sensory Acuity: Individuals with impaired vision or hearing may experience delays in detecting and responding to stimuli.
- Attention and Focus: Distractions and lack of attention can hinder the ability to perceive and respond to urgent stimuli.
- Physical Fitness: Individuals with good physical fitness, particularly in terms of hand-eye coordination and reflexes, may exhibit faster reaction times.
- Training and Experience: Regular training and exposure to urgent situations can improve reaction times through enhanced cognitive and muscular conditioning.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) leverage the 4-second rule to automate quick responses to hazards, enhancing vehicle safety.
- Robotics: Researchers are developing robots with sophisticated sensory systems and rapid decision-making algorithms, enabling them to interact effectively with humans in complex and urgent situations.
- Healthcare: Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems can provide real-time alerts and facilitate rapid response in medical emergencies, especially for patients with chronic conditions.
- “Interceptive Technologies” (a new term coined to describe technologies that intervene before an urgent situation arises): These technologies aim to predict and mitigate potential threats by analyzing data, identifying patterns, and alerting individuals or systems to take preemptive action.
- The 4-second rule: A review of the literature on the time required to initiate a rapid, accurate response to a novel, unexpected stimulus
- The 4-second rule in emergency response
- The role of the 4-second rule in sports performance
Emerging Applications and Innovations
The concept of the 4-second urgent time and distance is inspiring new applications and innovations across industries:
Conclusion
The 4-second urgent time and distance is a fundamental concept that shapes human perception, response, and interaction with the environment. Understanding and leveraging this principle can lead to advancements in various fields, such as traffic safety, emergency response, sports performance, and human-computer interaction. As technology and innovation continue to push boundaries, we can expect to see novel applications and solutions that harness the principles of urgent response to improve our lives and society.
Additional Resources
Tables
The following tables provide additional information and data related to the 4-second urgent time and distance:
| Age Group | Reaction Time (seconds) |
|---|---|
| Children (6-12 years) | 0.5 – 1.0 |
| Teenagers (13-19 years) | 0.4 – 0.8 |
| Adults (20-64 years) | 0.3 – 0.7 |
| Older Adults (65+ years) | 0.6 – 1.2 |
| Factor | Effect on Reaction Time |
|---|---|
| Age | Increases with age |
| Sensory Acuity | Decreases with impaired vision or hearing |
| Attention and Focus | Increased distraction leads to slower reaction times |
| Physical Fitness | Improved physical fitness leads to faster reaction times |
| Training and Experience | Regular training improves reaction times |
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Traffic Safety | Driver response to hazards |
| Emergency Response | First responder response times |
| Sports and Athletics | Athlete reaction time |
| Human-Computer Interaction | User interface response times |
| Autonomous Vehicles | Automated hazard response |
| Technology | Applications |
|---|---|
| Interceptive Technologies | Predicting and mitigating potential threats |
| Wearable Devices | Real-time alerts for medical emergencies |
| Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) | Automated vehicle response to hazards |
| Robotics | Rapid decision-making for human interaction |