Polar bears are carnivorous mammals that inhabit the Arctic regions. They are apex predators, meaning they sit at the top of the food chain. As such, they play a vital role in maintaining the health of the Arctic ecosystem.

Polar Bears’ Diet
Polar bears primarily feed on seals, which they hunt by lying in wait near breathing holes in the ice. They also eat walruses, whales, and other marine mammals. In addition to marine mammals, polar bears will also scavenge on carcasses left behind by other predators.
Trophic Level
In ecology, organisms are assigned to trophic levels based on their feeding habits. Primary consumers, or herbivores, eat plants. Secondary consumers, or carnivores, eat herbivores. Tertiary consumers, or top predators, eat other carnivores.
Polar bears are tertiary consumers because they eat other carnivores, such as seals and walruses. They are at the top of the food chain in the Arctic ecosystem.
Role in the Ecosystem
As top predators, polar bears play a vital role in the Arctic ecosystem. They help to keep populations of seals and walruses in check. This prevents these populations from becoming too large and overgrazing on the kelp forests that provide food and shelter for a variety of marine life.
Polar bears also help to maintain the health of the Arctic ecosystem by scavenging on carcasses. This helps to remove dead animals from the environment and prevents the spread of disease.
Threats to Polar Bears
Polar bears are facing a number of threats, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. Climate change is causing the Arctic sea ice to melt, which is reducing the amount of habitat available for polar bears. Habitat loss is also occurring due to the development of oil and gas resources in the Arctic. Pollution is another threat to polar bears, as they can ingest toxic chemicals through their food.
Conservation
Polar bears are a threatened species and are protected by law in many countries. Conservation efforts are focused on reducing the threats that polar bears face, such as climate change, habitat loss, and pollution.
Food Chain
The following is a simplified food chain that shows the position of polar bears in the Arctic ecosystem:
- Phytoplankton (primary producers)
- Zooplankton (primary consumers)
- Arctic cod (secondary consumers)
- Seals (tertiary consumers)
- Polar bears (apex predators)
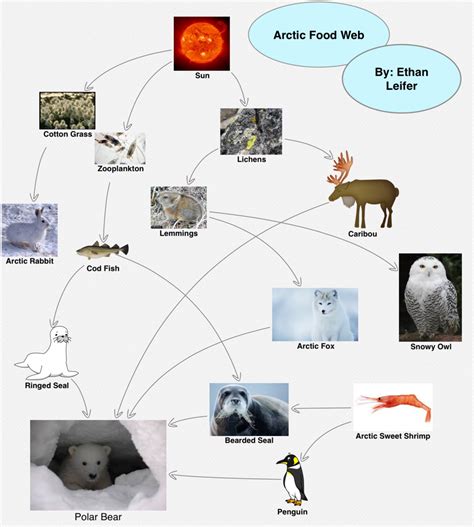
Food Web
Food webs are more complex than food chains, as they show the interconnected feeding relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem. The following is a simplified food web that shows the position of polar bears in the Arctic ecosystem:
[Image of a simplified food web showing the position of polar bears in the Arctic ecosystem]
As you can see, polar bears are connected to a variety of other organisms in the Arctic ecosystem. They are predators of seals, walruses, and other marine mammals. They are also scavengers, and they will eat carcasses left behind by other predators. Polar bears are also preyed upon by other predators, such as killer whales and wolves.
Polar bears play a vital role in the Arctic ecosystem. They are apex predators, meaning they sit at the top of the food chain. As such, they help to keep populations of seals and walruses in check. This prevents these populations from becoming too large and overgrazing on the kelp forests that provide food and shelter for a variety of marine life.
Polar bears also help to maintain the health of the Arctic ecosystem by scavenging on carcasses. This helps to remove dead animals from the environment and prevents the spread of disease.
Polar bears are facing a number of threats, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution.
Climate Change
Climate change is causing the Arctic sea ice to melt, which is reducing the amount of habitat available for polar bears. Polar bears rely on sea ice for hunting, breeding, and resting. As the sea ice melts, polar bears are forced to travel further to find food and shelter. This can lead to increased energy expenditure, which can make it difficult for polar bears to survive.
Habitat Loss
Habitat loss is also occurring due to the development of oil and gas resources in the Arctic. Oil and gas exploration and development can disrupt polar bear habitat and make it difficult for them to find food and shelter.
Pollution
Pollution is another threat to polar bears, as they can ingest toxic chemicals through their food. These chemicals can harm polar bears’ health and reproductive success.
Polar bears are a threatened species and are protected by law in many countries. Conservation efforts are focused on reducing the threats that polar bears face, such as climate change, habitat loss, and pollution.
One way to help conserve polar bears is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which contributes to climate change. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, we can help to slow the rate of climate change and protect polar bear habitat.
Another way to help conserve polar bears is to support sustainable development in the Arctic. Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Sustainable development practices can help to reduce habitat loss and pollution, which can benefit polar bears and other Arctic wildlife.
We can also help to conserve polar bears by supporting organizations that are working to protect them. These organizations are working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote sustainable development, and educate the public about the importance of polar bears.
Polar bears are a vital part of the Arctic ecosystem. They play a role in keeping populations of seals and walruses in check, and they help to maintain the health of the ecosystem by scavenging on carcasses. Polar bears are facing a number of threats, including climate change, habitat loss, and pollution. Conservation efforts are focused on reducing these threats and protecting polar bears for future generations.