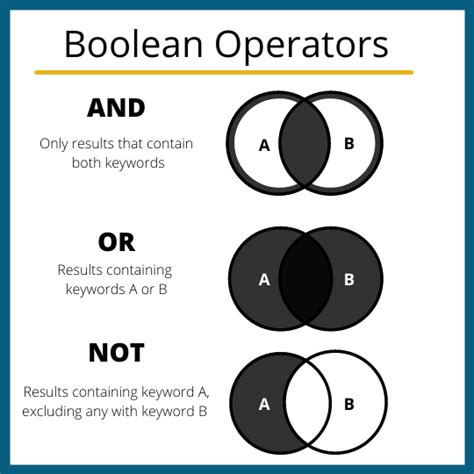
In the realm of online research and information retrieval, Boolean operators serve as powerful tools to refine and narrow down search queries. While the AND operator serves to identify documents that contain all specified terms, the NOT operator, also known as the negative operator, plays a crucial role in excluding unwanted or irrelevant results. This article delves into the intricacies of using the NOT operator in crossword puzzles, providing a comprehensive guide to leverage its capabilities effectively.

What is the NOT Operator?
The NOT operator, denoted by the symbol “-“, functions as an exclusionary filter in search queries. When used in conjunction with a keyword or term, it eliminates results that contain that particular word or phrase. This enables users to focus their search on specific topics while excluding irrelevant or distracting information.
Using the NOT Operator in Crossword Puzzles
Crossword puzzles often require solvers to find specific words or phrases that fit into a given grid. The NOT operator can be particularly useful in these scenarios, especially when dealing with common words or phrases that may appear in multiple locations within the puzzle. By excluding these common terms, solvers can narrow their focus and identify the correct answer more efficiently.
Example:
Consider a crossword puzzle clue that reads: “A type of fruit.” A solver may initially type in “apple” as a potential answer. However, if the grid already contains the word “apple” in another location, using the NOT operator can help exclude it from the search results. By entering “-apple,” the solver can retrieve a list of fruits that do not include the word “apple.” This approach increases the likelihood of finding the correct answer, which might be “banana” or “orange.”
Benefits of Using the NOT Operator
- Precision: Excluding unwanted terms enhances the precision of search results, leading to a more targeted and relevant list of potential answers.
- Efficiency: By eliminating irrelevant results, the NOT operator saves time and effort, allowing solvers to focus on the most promising options.
- Creativity: Negative boolean operator crosswording encourages users to think more creatively by considering alternative possibilities and exploring different word combinations.
Techniques for Effective NOT Operator Usage
- Identify Common Words: Pay attention to words that frequently appear in crossword puzzles, such as “the,” “a,” “in,” and “of.” Excluding these common terms can help narrow down the search results considerably.
- Use Synonyms: Consider using synonyms of the target word to expand the search. For example, instead of entering “-apple,” try “-fruit.” This approach increases the chances of finding the correct answer.
- Combine NOT with Other Operators: The NOT operator can be combined with other Boolean operators, such as AND and OR, to create more complex search queries. This versatility allows users to fine-tune their search parameters and maximize the efficiency of their crossword-solving process.
Applications Beyond Crossword Puzzles
The negative boolean operator is not limited to crossword puzzles. Its versatility extends to various other applications:
- Online Research: Excluding specific terms or phrases can help researchers eliminate irrelevant information and focus on the most relevant sources.
- Database Queries: Databases can be optimized by using the NOT operator to exclude duplicate entries or filter out irrelevant data.
- Spam Filtering: Email filters can incorporate the NOT operator to block messages containing specific keywords or phrases, reducing the incidence of unwanted emails.
Conclusion
The negative boolean operator, or NOT operator, plays a vital role in crossword puzzles by enabling solvers to exclude unwanted terms and refine their search results. By leveraging its capabilities effectively, crossword enthusiasts can enhance their precision, efficiency, and creativity in solving puzzles. The applications of the NOT operator extend beyond crossword puzzles, demonstrating its versatility in various domains where information retrieval and filtering are essential.