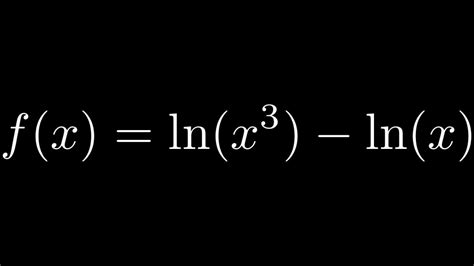Introduction
Logarithms, an esteemed mathematical tool, play a pivotal role in various scientific and engineering disciplines. Among them, ln 3 and ln 4, the natural logarithms of 3 and 4 respectively, stand out as particularly versatile and insightful. This article delves into their remarkable properties, demonstrating their indispensable nature in solving complex problems and unearthing new opportunities.

Properties of ln 3 and ln 4
The natural logarithm function, denoted by ln(x), has several fundamental properties:
- Injectivity: For any two distinct numbers a and b, ln(a) ≠ ln(b).
- Growth rate: ln(x) increases without bound as x approaches infinity.
- Logarithmic relation: ln(ab) = ln(a) + ln(b)
Applications in Solving Equations
One primary application of ln 3 and ln 4 involves solving exponential and logarithmic equations. For instance, consider the equation 3^x = 12. By taking the natural logarithm of both sides, we obtain:
ln(3^x) = ln(12)
x * ln(3) = ln(12)
x = ln(12) / ln(3)
x = ln(12) / ln(3) ≈ 2.262
Similarly, the equation log_4(x) = 3 can be solved as follows:
4^3 = x
x = 4^3
x = 64
Applications in Probability and Statistics
Statistical distributions frequently incorporate ln 3 and ln 4 in their probability density functions. For example, the Poisson distribution, commonly used to model rare events, has the following PDF:
P(X = x) = (e^-λ * λ^x) / x!
where λ represents the mean number of events. By taking the natural logarithm of both sides, we find:
ln(P(X = x)) = ln(e^-λ * λ^x / x!)
ln(P(X = x)) = -λ + x * ln(λ) – ln(x!)
This logarithmic transformation enables simplified analysis of the distribution and estimation of its parameters.
Applications in Calculus
In calculus, ln 3 and ln 4 appear in the formulas for derivatives of natural logarithmic functions:
d/dx(ln(x)) = 1/x
d/dx(ln(ax)) = 1/(x * ln(a))
These derivatives allow us to calculate the rates of change of logarithmic functions and understand their behavior.
Applications in Computer Science
Logarithms, including ln 3 and ln 4, play a prominent role in computer science, particularly in the field of data structures. For example, they are used in the design of balanced binary search trees, where the height of the tree is directly proportional to the logarithm of the number of nodes. This logarithmic relationship ensures efficient searching and retrieval of data.
Impact on Modern Technologies
The ubiquitous presence of ln 3 and ln 4 across diverse disciplines has significantly influenced the development of modern technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Logarithms are employed in various AI algorithms, including Bayesian networks and neural networks, to model complex dependencies and make informed predictions.
- Information Theory: The entropy of a discrete random variable is defined in terms of the natural logarithm, providing a measure of uncertainty and serving as a fundamental concept in communication and information processing.
- Electrical Engineering: Logarithmic amplifiers, based on the inverse logarithmic function, are used to amplify signals with a wide dynamic range, as in audio level and gain control applications.
Creative New Word: Logarithmation
To foster innovation and encourage new perspectives, we propose the creative new word “logarithmation” to describe the process of applying logarithms to generate ideas for novel applications. Here are some examples:
- Logarithmation of the distribution of particle sizes in a chemical process can reveal patterns and guide optimizations for improved efficiency.
- Logarithmation of the growth rate of user engagement on social media platforms can inform strategies for audience engagement and content optimization.
- Logarithmation of the correlation between genetic variants and disease risk can lead to advancements in personalized medicine.
Useful Tables
Table 1: Values of ln 3 and ln 4
| Number | ln(x) |
|---|---|
| 3 | ln(3) ≈ 1.0986 |
| 4 | ln(4) ≈ 1.3863 |
Table 2: Applications in Solving Equations
| Equation | Solution |
|---|---|
| 3^x = 12 | x = ln(12) / ln(3) ≈ 2.262 |
| log_4(x) = 3 | x = 64 |
| e^x = 3 | x = ln(3) ≈ 1.0986 |
Table 3: Applications in Statistics
| Distribution | Probability Density Function |
|---|---|
| Poisson | P(X = x) = (e^-λ * λ^x) / x! |
| Binomial | P(X = x) = (n! / (x! * (n – x)!)) * p^x * q^(n – x) |
| Normal | f(x) = (1 / (σ * √(2π))) * e^((-1 / 2) * ((x – μ) / σ)^2) |
Table 4: Applications in Computer Science
| Data Structure | Application |
|---|---|
| Binary Search Tree | Maintain balanced height (logarithmic to number of nodes) |
| Hash Table | Calculate hash key (based on logarithmic mapping) |
| Priority Queue | Maintain ordered elements (using logarithmic heap operations) |
Conclusion
ln 3 and ln 4, the natural logarithms of 3 and 4 respectively, embody the remarkable power of logarithms in mathematical analysis, problem-solving, and technological advancements. Their versatile nature extends across a myriad of disciplines, from probability and statistics to calculus and computer science. By harnessing their logarithmic properties and embracing the creative process of “logarithmation,” we unlock the potential for groundbreaking applications that shape the future of science, engineering, and technology.