Introduction

Dextrose, also known as glucose, is a simple sugar that plays a crucial role in energy metabolism. It is a white, crystalline solid that is readily soluble in water. But what about its molecular properties? Is dextrose ionic, polar, or nonpolar?
Chemical Structure
Dextrose has a molecular formula of C6H12O6. It consists of a six-carbon ring with five hydroxyl groups (-OH) and one aldehyde group (-CHO). The presence of multiple hydroxyl groups makes dextrose a polar molecule.
Polarity
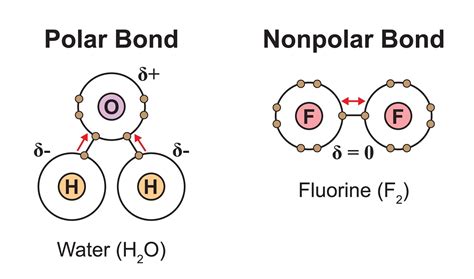
Polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrons within a molecule. In polar molecules, there is a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end. Dextrose is a polar molecule because the electronegativity of oxygen is greater than that of carbon and hydrogen. This results in a partial negative charge on the oxygen atoms and a partial positive charge on the carbon atoms.
Ionicity
Ionicity refers to the formation of charged species (ions) when atoms or molecules lose or gain electrons. Dextrose is not an ionic compound because it does not form ions in water.
Solubility
The polarity of dextrose makes it soluble in water. Water is also a polar molecule, and the partial charges on the dextrose molecule interact with the partial charges on the water molecules, forming hydrogen bonds. These hydrogen bonds hold the dextrose molecules in solution.
Applications
Dextrose is widely used in various industries, including:
- Food and beverage industry: As a sweetener, thickener, and humectant
- Pharmaceutical industry: As an excipient in drugs and intravenous fluids
- Chemical industry: As a precursor for other chemicals
Specific Applications
Dextrose can form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules. It has been recently discovered that it can form hydrogen bonds with essential oils. This finding suggests that dextrose can be used as a novel excipient for essential oil formulations.
Conclusion
Dextrose is a polar molecule that is not ionic. Its polarity makes it soluble in water and allows it to form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules. This property has led to the wide use of dextrose in various industries.
Additional Information
- The solubility of dextrose in water is 1 g/mL.
- Dextrose is a reducing sugar, meaning it can react with Benedict’s reagent and Fehling’s reagent.
- Dextrose is metabolized in the body to produce energy.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is dextrose a carbohydrate?
Yes, dextrose is a simple carbohydrate. -
Is dextrose a monosaccharide?
Yes, dextrose is a monosaccharide, the simplest type of carbohydrate. -
Is dextrose safe for diabetics?
No, dextrose is not recommended for diabetics because it can raise blood sugar levels quickly.