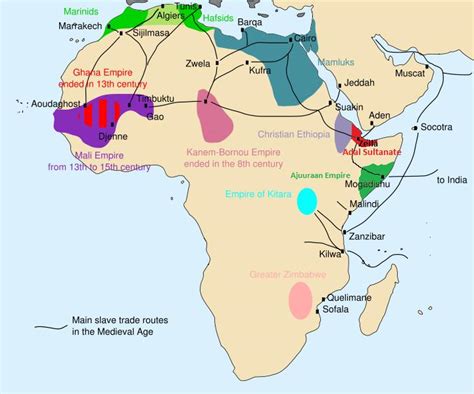
Slavery in the Arab world has a long and complex history, dating back to the pre-Islamic era. During the Islamic Golden Age, the Arab slave trade expanded dramatically, and enslaved people became a major commodity.

The Scale of the Arab Slave Trade
The exact number of enslaved people in the Arab world is unknown, but estimates range from 10 to 20 million. The majority of these enslaved people were from Africa, but they also came from other regions, such as Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
The Treatment of Enslaved People
The treatment of enslaved people varied depending on their status and the region in which they lived. Some enslaved people were treated as property, while others were given more freedom and responsibility. In general, however, enslaved people were subject to physical and sexual abuse, and they were often forced to work long hours in dangerous conditions.
The Abolition of Slavery in the Arab World
Slavery was gradually abolished in the Arab world throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. The first country to abolish slavery was Tunisia, in 1846. Other countries followed suit, and by the early 20th century, slavery had been abolished in most of the Arab world.
However, slavery persists in some parts of the Arab world today. In Mauritania, for example, it is estimated that there are still thousands of enslaved people. The government of Mauritania has taken steps to address this issue, but it remains a challenge.
The Legacy of Slavery
The legacy of slavery in the Arab world is still felt today. Many of the social and economic inequalities that exist in the Arab world can be traced back to the history of slavery. Additionally, the experiences of enslaved people in the Arab world have had a profound impact on the culture and literature of the region.
- The Arab slave trade was a major economic force in the Arab world for centuries.
- The majority of enslaved people in the Arab world were from Africa.
- The treatment of enslaved people varied depending on their status and the region in which they lived.
- Slavery was gradually abolished in the Arab world throughout the 19th and 20th centuries.
- The legacy of slavery in the Arab world is still felt today.
The Arab slave trade had a profound impact on the Arab world. It shaped the region’s economic, social, and political landscape.
Economic Impact
The Arab slave trade was a major economic force in the Arab world. It generated huge profits for slave traders and plantation owners. The slave trade also led to the development of new industries, such as the textile industry.
Social Impact
The Arab slave trade had a major impact on Arab society. It created a new social hierarchy, with enslaved people at the bottom. The slave trade also led to the spread of new diseases and the disruption of traditional family structures.
Political Impact
The Arab slave trade had a major impact on Arab politics. It led to the rise of new political elites and the decline of others. The slave trade also contributed to the instability of the Arab world.
Cultural Impact
The Arab slave trade had a major impact on Arab culture. It influenced the region’s art, music, and literature. The slave trade also shaped the Arab world’s view of itself and its place in the world.
The abolition of slavery in the Arab world was a long and complex process. It began in the early 19th century with the efforts of reformers such as Muhammad Ali Pasha of Egypt. However, the abolition of slavery was not fully achieved until the early 20th century.
There were a number of factors that contributed to the abolition of slavery in the Arab world. One factor was the pressure from European powers. Another factor was the rise of Arab nationalism. Finally, the abolition of slavery was also driven by the growing humanitarian sentiment in the Arab world.
The abolition of slavery in the Arab world was a major turning point in the history of the region. It marked the end of a centuries-old institution that had a profound impact on Arab society. The abolition of slavery also paved the way for the development of a more just and equitable society in the Arab world.
The legacy of slavery in the Arab world is still felt today. Many of the social and economic inequalities that exist in the Arab world can be traced back to the history of slavery. Additionally, the experiences of enslaved people in the Arab world have had a profound impact on the culture and literature of the region.
The legacy of slavery in the Arab world is a complex and challenging one. However, it is important to remember that the abolition of slavery was a major step forward for the region. The Arab world has made great progress in the years since slavery was abolished, and it is important to continue to build on this progress.
Table 1: Number of Enslaved People in the Arab World
| Region | Number of Enslaved People |
|---|---|
| North Africa | 5-10 million |
| West Africa | 2-5 million |
| East Africa | 1-2 million |
| Central Africa | 1-2 million |
| South Africa | 1-2 million |
Table 2: Treatment of Enslaved People in the Arab World
| Status | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Chattel slaves | Treated as property, subject to physical and sexual abuse, forced to work long hours in dangerous conditions |
| Household slaves | Given more freedom and responsibility, often treated as members of the family |
| Concubines | Sex slaves, often kept in seclusion |
| Soldiers | Trained to fight in the armies of their masters |
Table 3: Abolition of Slavery in the Arab World
| Country | Year of Abolition |
|---|---|
| Tunisia | 1846 |
| Morocco | 1925 |
| Algeria | 1925 |
| Libya | 1962 |
| Egypt | 1964 |
| Sudan | 1967 |
| Saudi Arabia | 1962 |
| Yemen | 1967 |
Table 4: The Legacy of Slavery in the Arab World
| Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Social inequality | Enslaved people and their descendants often face discrimination and disadvantage |
| Economic inequality | Enslaved people and their descendants often have lower incomes and less access to education and healthcare |
| Political instability | The history of slavery has contributed to political instability in the Arab world |
| Cultural impact | The experiences of enslaved people have influenced the art, music, and literature of the Arab world |