Introduction
A sulfide ion plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions, owing to its unique charge. Understanding its charge is essential for comprehending its behavior and applications in numerous fields.

Sulfide Ion: Definition and Structure
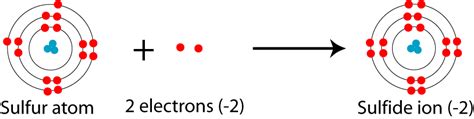
A sulfide ion (S²⁻) is an anion that contains a sulfur atom (S) with a formal charge of -2. It is formed when a sulfur atom gains two electrons, resulting in an overall negative charge.
Determining the Charge of a Sulfide Ion
The charge of a sulfide ion can be determined using the following steps:
- Identify the number of valence electrons in a sulfur atom. Sulfur has six valence electrons.
- Determine the number of electrons lost or gained by the sulfur atom. In the case of a sulfide ion, the sulfur atom gains two electrons.
- Determine the formal charge by subtracting the number of valence electrons from the number of electrons in the ion. In this case, 6 – 8 = -2.
Therefore, a sulfide ion has a formal charge of -2.
Chemical Properties of Sulfide Ion
The charge of a sulfide ion influences its chemical properties, which include:
Reactivity:
Sulfide ions are highly reactive due to their negative charge. They readily react with metal ions to form metal sulfides, which are often insoluble in water.
Formation of Acidic Solutions:
Sulfide ions react with water to form hydrosulfide ions (HS⁻) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻), resulting in a slightly acidic solution.
Oxidative Potential:
Sulfide ions are easily oxidized to form elemental sulfur or sulfate ions (SO4²⁻).
Applications of Sulfide Ion
The unique charge and chemical properties of sulfide ions make them valuable in several applications, such as:
Mining and Metallurgy:
- Sulfide ores are mined to extract metals such as copper, zinc, and lead.
- Sulfide ions are used as flotation agents in ore processing, helping to separate valuable minerals from waste materials.
Paper Production:
- Sulfide ions are used in the Kraft process to break down lignin in wood, making it easier to produce paper pulp.
Chemical Synthesis:
- Sulfide ions are used as reducing agents in the synthesis of various organic compounds, such as dyes and pharmaceuticals.
Case Study: Sulfide Ion in Wastewater Treatment
In wastewater treatment, sulfide ions pose a challenge due to their toxicity and odor problems. The charge of sulfide ions influences their behavior in wastewater systems, as follows:
- Odor Formation: Sulfide ions react with hydrogen ions to form hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S), which has a characteristic “rotten egg” smell.
- Toxicity to Microorganisms: Sulfide ions can inhibit the growth of microorganisms used in biological wastewater treatment processes, reducing treatment efficiency.
Management of sulfide ions in wastewater involves:
- Acidification: Lowering the pH of wastewater reduces the formation of hydrogen sulfide gas.
- Aeration: Introducing oxygen into wastewater oxidizes sulfide ions to less toxic sulfate ions.
- Chemical Precipitation: Adding metal salts, such as ferric chloride, precipitates sulfide ions as insoluble metal sulfides.
Strategies for Reducing Waste and Increasing Efficiency
Conclusion
The charge of a sulfide ion is a fundamental property that governs its chemical behavior and applications. With an understanding of its charge and properties, scientists and engineers can harness sulfide ions to solve problems and develop innovative solutions in fields such as metallurgy, paper production, chemical synthesis, and wastewater treatment.