Introduction

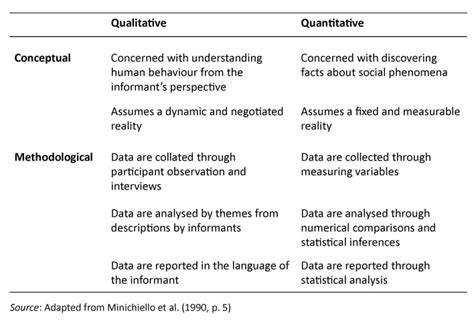
In the realm of psychology, research plays a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of the human mind and behavior. Two fundamental approaches to gathering data in psychology are qualitative and quantitative research. Each approach offers unique strengths and applications, providing researchers with a comprehensive toolkit for investigating psychological phenomena.
Qualitative Data: Exploring the Depths
-
What is Qualitative Data?
Qualitative data consists of non-numerical information that captures the subjective experiences, perspectives, and meanings of individuals or groups. It involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, participant observation, and document analysis. -
Advantages:
- Rich and detailed
- Uncovers hidden meanings and motivations
- Provides insights into individual experiences and social contexts
- Explores complex and nuanced phenomena
-
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming to collect and analyze
- Subjective and prone to researcher bias
- Generalizability limited due to small sample sizes
Quantitative Data: Measuring the Measureable
-
What is Quantitative Data?
Quantitative data is numerical information that can be analyzed statistically to identify patterns, test hypotheses, and draw conclusions. It involves surveys, experiments, and physiological measures. -
Advantages:
- Objective and reliable
- Allows for statistical analysis and hypothesis testing
- Generalizable to larger populations
- Can quantify specific behaviors and measure change
-
Disadvantages:
- Limited to what can be observed and measured
- May miss out on contextual and subjective factors
- Can be influenced by confounding variables
Choosing the Right Approach
The choice between qualitative and quantitative data depends on the research question and the nature of the phenomenon being studied.
- Qualitative: Suitable for exploring experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and social contexts where in-depth understanding is needed.
- Quantitative: Ideal for testing hypotheses, establishing cause-and-effect relationships, and measuring specific behaviors.
Combining Approaches: Triangulation and Mixed Methods
Researchers often combine qualitative and quantitative methods in a process known as triangulation or mixed methods. This approach enhances the strengths and minimizes the limitations of both methodologies.
Applications of Qualitative and Quantitative Data
-
Qualitative:
- Case studies: Understanding individual experiences
- Ethnographies: Observing and describing cultures and subcultures
- Phenomenology: Exploring subjective experiences of a phenomenon
-
Quantitative:
- Experiments: Testing hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships
- Surveys: Gathering data from large populations
- Neuroimaging: Measuring brain activity during psychological processes
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Qualitative | Quantitative |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Non-numerical | Numerical |
| Collection Methods | Interviews, focus groups, observation | Surveys, experiments, physiological measures |
| Analysis | Interpretation, theme identification | Statistical analysis, hypothesis testing |
| Goals | Exploration, understanding | Measurement, testing |
| Strengths | Rich, subjective | Objective, generalizable |
| Weaknesses | Time-consuming, subjective | Limited scope, may miss out on context |
Tips for Conducting Research
- Clearly define your research question and goals. This will determine the appropriate data collection method.
- Choose a sampling method that represents the target population. Ensure a diverse and representative sample for qualitative research.
- Use valid and reliable data collection tools. Design surveys and experiments carefully to avoid bias.
- Analyze data using appropriate methods. Use qualitative software for qualitative data and statistical software for quantitative data.
- Interpret results with objectivity and consider limitations. Acknowledge the strengths and weaknesses of your research approach.
Conclusion
Qualitative and quantitative data are essential tools in AP Psychology research. By understanding the differences and strengths of each approach, researchers can choose the most appropriate method for their research question. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods can provide a comprehensive understanding of psychological phenomena, enabling us to delve deeper into the complexities of the human mind and behavior.