Introduction
Fiscal policy, a fundamental pillar of macroeconomic management, involves the use of government spending and taxation to influence economic activity. This unit delves into the intricate relationship between fiscal policy and aggregate demand (AD), exploring their impact on macroeconomic variables such as output, employment, inflation, and economic growth.

Fiscal Policy Tools
The government has two primary fiscal policy tools at its disposal:
- Government Spending: Increases in government spending boost aggregate demand by injecting money into the economy.
- Taxation: Tax cuts increase disposable income, stimulating consumption and investment, while tax hikes reduce AD by reducing disposable income.
Impact of Fiscal Policy on Aggregate Demand
Fiscal policy affects AD through the following channels:
- Government Spending Multiplier: Each dollar of government spending increases AD by a multiple greater than one, as it generates ripple effects through the economy.
- Tax Multiplier: Tax cuts increase AD by a multiple greater than the tax cut itself, stimulating spending. Tax hikes have the opposite effect.
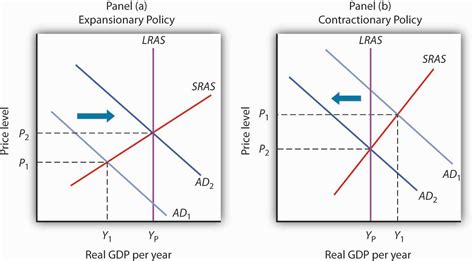
Expansionary vs. Contractionary Fiscal Policy
- Expansionary Fiscal Policy: Aims to increase AD by increasing government spending or cutting taxes. This policy is typically used during economic downturns to boost output and employment.
- Contractionary Fiscal Policy: Aims to decrease AD by reducing government spending or raising taxes. This policy is typically used to curb inflation or reduce government debt.
The Balanced Budget Multiplier
The balanced budget multiplier refers to the impact on AD when the government increases both spending and taxes by the same amount. The net effect on AD depends on the relative magnitudes of the spending and tax changes.
Short-Run and Long-Run Effects
Fiscal policy can have both short-run and long-run effects:
- Short-Run: Fiscal policy can quickly impact AD and macroeconomic variables in the short term.
- Long-Run: Over time, the long-run effects of fiscal policy may differ from the short-run effects, particularly if the policy leads to changes in government debt.
Crowding Out
- Investment Crowding Out: Expansionary fiscal policy can lead to higher interest rates, which may reduce private investment and offset some of the AD increase.
- Government Consumption Crowding Out: Government spending can compete with private consumption, leading to reduced private consumption.
Effective Strategies for Fiscal Policy
To maximize the effectiveness of fiscal policy, policymakers should consider the following strategies:
- Timing: Fiscal policy should be implemented during economic downturns to stimulate AD and during economic expansions to curb inflation.
- Size: The magnitude of fiscal policy should be sufficient to achieve the desired macroeconomic outcome without excessive crowding out.
- Composition: The composition of fiscal policy (spending vs. taxation) should be tailored to specific economic conditions and long-term goals.
Real-World Examples
- Great Recession (2008-2009): Massive expansionary fiscal policy helped mitigate the economic crisis, including the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009.
- European Debt Crisis (2010-2015): Austerity measures (contractionary fiscal policy) in Europe exacerbated the crisis by reducing AD.
How to Apply Fiscal Policy in Practice
- Identify Economic Objectives: Determine the macroeconomic goals, such as increasing output, reducing unemployment, or controlling inflation.
- Choose Fiscal Policy Tools: Select the appropriate fiscal policy tools (spending, taxation) based on the economic objectives and constraints.
- Estimate Multipliers: Calculate the potential impact of the policy changes on AD using the appropriate multipliers.
- Monitor and Adjust: Track economic indicators and adjust fiscal policy as needed to achieve the desired outcomes.
FAQs about AP Macro Unit 4
-
What is the difference between expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy?
Expansionary fiscal policy increases AD by increasing spending or cutting taxes, while contractionary fiscal policy decreases AD by reducing spending or raising taxes. -
What is the balanced budget multiplier?
The balanced budget multiplier is the effect on AD when the government simultaneously increases spending and taxes by the same amount. -
What is crowding out?
Crowding out occurs when government spending or borrowing competes with private investment or consumption, reducing AD. -
How does fiscal policy affect economic growth in the long run?
Fiscal policy can affect economic growth in the long run by influencing investment, capital formation, and government debt accumulation. -
What are some real-world examples of the use of fiscal policy?
Examples include the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 during the Great Recession and austerity measures in Europe during the European Debt Crisis. -
How can policymakers improve the effectiveness of fiscal policy?
Policymakers can enhance the effectiveness of fiscal policy by considering the timing, size, and composition of the policy, as well as potential crowding-out effects. -
What are the limitations of fiscal policy?
Limitations include the potential for inflationary pressures, long-term effects on government debt, and political constraints. -
How does fiscal policy interact with monetary policy?
Fiscal policy and monetary policy work together to manage aggregate demand, with fiscal policy targeting long-term economic goals and monetary policy focusing on short-term stability.
Tables
| Fiscal Policy Tool | Effect on Aggregate Demand |
|---|---|
| Government Spending | Increases AD |
| Tax Cuts | Increases AD by stimulating spending |
| Tax Hikes | Decreases AD by reducing disposable income |
| Type of Fiscal Policy | Impact on Output and Employment |
|---|---|
| Expansionary | Increases output and employment |
| Contractionary | Decreases output and employment |
| Multiplier Effect | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Government Spending Multiplier | ΔGDP = (1 / (1 – MPC)) * ΔG |
| Tax Multiplier | ΔGDP = (MPC / (1 – MPC)) * ΔT |
| Crowding Out Effect | Economic Impact |
|---|---|
| Investment Crowding Out | Reduces private investment |
| Government Consumption Crowding Out | Reduces private consumption |