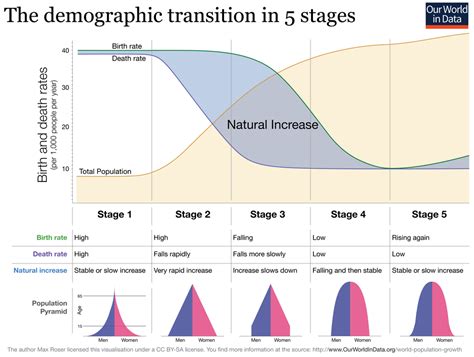
The rate of natural increase (RNI) is a measure of the change in a population over time due to the difference between birth rates and death rates. It is calculated as the difference between the crude birth rate (CBR) and the crude death rate (CDR).

$$RNI = CBR – CDR$$
A positive RNI indicates that the population is growing, while a negative RNI indicates that the population is declining. The RNI can be used to project future population growth or decline and to inform policy decisions related to population management.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Natural Increase
The RNI is influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Fertility rates: The number of children born per woman.
- Mortality rates: The number of deaths per 1,000 people.
- Migration rates: The number of people moving into or out of a population.
- Age structure of the population: The proportion of people in different age groups.
Global Trends in the Rate of Natural Increase
The global RNI has been declining in recent decades. According to the World Bank, the global RNI was 1.1% in 2020, down from 2.1% in 1970. This decline is due to a combination of factors, including declining fertility rates and increasing life expectancy.
Regional Variations in the Rate of Natural Increase
The RNI varies significantly across regions of the world. In 2020, the RNI was highest in sub-Saharan Africa (2.7%) and lowest in Europe (0.1%). These regional variations are due to differences in fertility rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns.
Implications of the Rate of Natural Increase
The RNI has important implications for a variety of societal issues, including:
- Economic growth: A high RNI can lead to a rapid increase in the size of the workforce, which can contribute to economic growth.
- Social services: A high RNI can put strain on social services, such as education and healthcare.
- Environmental sustainability: A high RNI can contribute to environmental degradation, such as deforestation and pollution.
Policy Considerations
Governments can use a variety of policies to influence the RNI, including:
- Family planning programs: These programs provide access to contraception and other reproductive health services.
- Education: Raising educational attainment levels can lead to lower fertility rates.
- Healthcare: Improving healthcare can lead to lower mortality rates.
- Immigration: Governments can increase or decrease immigration rates to influence the size and composition of the population.
Conclusion
The rate of natural increase is a measure of the change in a population over time due to the difference between birth rates and death rates. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including fertility rates, mortality rates, migration rates, and the age structure of the population. The RNI has important implications for a variety of societal issues, including economic growth, social services, environmental sustainability, and policy considerations.
FAQs:
- What is the formula for calculating the rate of natural increase?
RNI = CBR - CDR
- What are some of the factors that affect the rate of natural increase?
- Fertility rates
- Mortality rates
- Migration rates
- Age structure of the population
- What are some of the regional variations in the rate of natural increase?
- The RNI is highest in sub-Saharan Africa (2.7%) and lowest in Europe (0.1%).
- What are some of the implications of the rate of natural increase?
- Economic growth
- Social services
- Environmental sustainability
- What are some of the policy considerations related to the rate of natural increase?
- Family planning programs
- Education
- Healthcare
- Immigration
- How can the rate of natural increase be used to project future population growth or decline?
- The RNI can be used to project future population growth or decline by using population models that take into account the factors that affect the RNI.