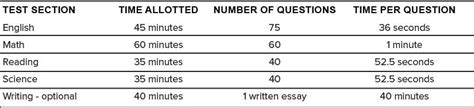
The ACT (American College Testing) is a standardized admissions test for college-bound students in the United States. It is a multiple-choice test and consists of four sections: English, Mathematics, Reading, and Science.

The standard testing time for the ACT is 3 hours and 35 minutes. However, students with certain disabilities or accommodations may be eligible for extended time on the ACT.
Extended Time Eligibility
Students with the following disabilities or accommodations may be eligible for extended time on the ACT:
- Visual impairment
- Hearing impairment
- Dyslexia
- ADHD
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Traumatic brain injury
- Other medical conditions that affect the ability to take the test
Extended Time Length
The length of extended time that a student is granted depends on their specific disability or accommodation. The following are the most common extended time accommodations:
| Disability or Accommodation | Extended Time Length |
|---|---|
| Visual impairment | 25% additional time |
| Hearing impairment | 50% additional time |
| Dyslexia | 50% additional time |
| ADHD | 50% additional time |
| Autism spectrum disorder | 100% additional time |
| Traumatic brain injury | 100% additional time |
How to Request Extended Time
To request extended time on the ACT, students must submit documentation of their disability or accommodation from a qualified professional. The documentation must be submitted to ACT, Inc. at least 30.days before the test date.
Benefits of Extended Time
Extended time can help students with disabilities or accommodations to complete the ACT test without feeling rushed or overwhelmed. This can lead to improved test scores and a better chance of being admitted to their desired college.
Tips for Using Extended Time
Students who are granted extended time on the ACT should use it wisely. The following tips can help:
- Arrive at the testing center early.
- Bring all necessary materials, including a watch, pencils, and erasers.
- Start each section of the test on time.
- Take breaks as needed.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help from the test administrator.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Students who are granted extended time on the ACT should avoid the following common mistakes:
- Starting sections of the test late.
- Taking too many breaks.
- Not using all of the extended time.
- Getting discouraged if they don’t finish all of the questions.
FAQs
Q: How long is the ACT test with extended time?
A: The length of extended time that a student is granted depends on their specific disability or accommodation, but it can range from 25% additional time to 100% additional time.
Q: Who is eligible for extended time on the ACT?
A: Students with visual impairment, hearing impairment, dyslexia, ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, traumatic brain injury, or other medical conditions that affect their ability to take the test may be eligible for extended time.
Q: How do I apply for extended time on the ACT?
A: To apply for extended time on the ACT, students must submit documentation of their disability or accommodation from a qualified professional to ACT, Inc. at least 30.days before the test date.
Q: What are the benefits of extended time on the ACT?
A: Extended time can help students with disabilities or accommodations to complete the ACT test without feeling rushed or overwhelmed, which can lead to improved test scores and a better chance of being admitted to their desired college.