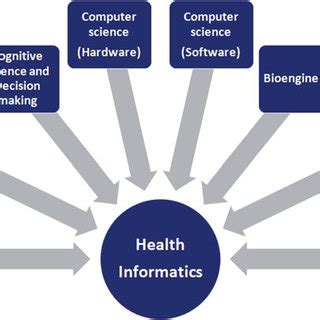
Introduction
In the modern healthcare landscape, health informatics has emerged as an indispensable field that plays a vital role in improving patient care, streamlining healthcare processes, and advancing medical knowledge. Health informatics professionals are responsible for a wide range of duties that encompass both technical and interpersonal skills. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the duties of health informatics professionals, highlighting their critical contributions to the healthcare industry.

Technical Responsibilities
1. Data Management and Analysis
Health informatics professionals are responsible for managing and analyzing vast amounts of patient data, including medical records, lab results, and imaging studies. They use data analysis tools to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that can lead to improved diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
- According to the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), the demand for health informatics professionals is expected to grow by 20% by 2030.
- Health informatics professionals typically earn an average annual salary of $91,550, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
2. Systems Implementation and Integration
Health informatics professionals design, implement, and maintain health information systems (HIS) and electronic health records (EHRs). They work closely with clinicians, administrators, and technical staff to ensure that HISs and EHRs meet the specific needs of healthcare organizations.
3. Healthcare Application Development
Health informatics professionals develop innovative healthcare applications that leverage data and technology to improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare processes. These applications range from patient portals to clinical decision support systems.
4. Data Security and Privacy
Health informatics professionals play a crucial role in ensuring the security and privacy of patient data. They implement and monitor data security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect patient information from unauthorized access or breaches.
Interpersonal Responsibilities
1. Collaboration and Communication
Health informatics professionals work closely with a variety of individuals, including clinicians, administrators, patients, and vendors. They effectively communicate complex technical concepts and collaborate with others to develop and implement health information systems.
2. Education and Training
Health informatics professionals provide education and training to clinicians and other healthcare staff on the use of health information systems and technologies. They ensure that healthcare professionals are proficient in utilizing these tools to improve patient care.
3. Patient Advocacy
Health informatics professionals advocate for patients’ rights and interests regarding their health information. They ensure that patients have access to their medical records and that their privacy is protected.
4. Quality Improvement
Health informatics professionals monitor and evaluate the use of health information systems and technologies to identify areas for improvement. They work with healthcare organizations to optimize HISs and EHRs, leading to better patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare processes.
Emerging Duties**
With the rapid advancements in healthcare technology, health informatics professionals are embracing new duties, including:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Health informatics professionals leverage AI and ML to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and develop personalized medicine.
2. Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
Health informatics professionals support the implementation and use of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring technologies to expand access to healthcare services.
3. Blockchain Technology
Health informatics professionals explore the use of blockchain technology to secure patient data and facilitate data sharing among healthcare providers.
Evolving Opportunities
The field of health informatics continues to evolve, creating exciting opportunities for professionals. Consider these emerging areas:
1. Health Informatics Risk Management
Health informatics professionals assess and manage risks associated with healthcare information systems and data.
2. Decision Analytics
Health informatics professionals use data analysis techniques to improve healthcare decision-making for patients, clinicians, and healthcare organizations.
3. Informatics Nursing
Nurses with advanced knowledge in health informatics play a vital role in implementing and using EHRs and other health technologies to enhance patient care.
4. Health Data Science
Health informatics professionals with a strong background in data science use advanced statistical and computational techniques to extract meaningful insights from healthcare data.
Job Outlook and Salary**
The job outlook for health informatics professionals is exceptionally bright. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the demand for health information technicians is expected to grow by 11% by 2030, much faster than the average for all occupations. The median annual salary for health information technicians is $47,620.
Conclusion**
Health informatics professionals play a multifaceted and indispensable role in modern healthcare. Their technical and interpersonal skills enable them to manage data effectively, implement health information systems, develop healthcare applications, ensure data security and privacy, and improve the quality of patient care. As the healthcare industry evolves, health informatics professionals will continue to embrace emerging technologies and assume new duties to meet the ever-changing needs of patients and healthcare organizations.
1. Improved Patient Outcomes
Health informatics systems provide clinicians with access to real-time patient data, facilitating better diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
2. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
Health informatics tools streamline healthcare processes, reducing paperwork, automating tasks, and improving communication among healthcare providers.
3. Reduced Costs
By reducing medical errors, improving efficiency, and preventing unnecessary tests and procedures, health informatics can significantly reduce healthcare costs.
4. Increased Patient Satisfaction
Health informatics systems empower patients with access to their medical records and online portals, enhancing their involvement in their care and improving their satisfaction.
5. Advanced Medical Research
Health informatics professionals play a vital role in medical research by collecting, analyzing, and interpreting large amounts of healthcare data to advance medical knowledge and improve patient care.
1. Data Interoperability
Ensuring seamless data exchange and interoperability among different health information systems remains a challenge.
2. Data Privacy and Security
Protecting patient data from unauthorized access and breaches is a critical concern in health informatics.
3. Lack of Qualified Professionals
The healthcare industry faces a shortage of qualified health informatics professionals to meet the growing demand.
4. Resistance to Change
Overcoming resistance to change and adopting new health information technologies can be challenging for some healthcare professionals.
5. Ethical Considerations
Health informatics professionals must navigate ethical considerations related to patient privacy, data ownership, and the use of artificial intelligence in healthcare.
1. What is the role of a health informatics professional?
Health informatics professionals use technology and data to improve healthcare processes, enhance patient care, and advance medical research.
2. What skills are required to be a health informatics professional?
Health informatics professionals require a blend of technical skills (data analysis, systems implementation) and interpersonal skills (communication, collaboration).
3. What is the job outlook for health informatics professionals?
The job outlook is positive, with a projected growth of 11% by 2030, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
4. What is the average salary for health informatics professionals?
The median annual salary for health information technicians is $47,620.
5. What are some emerging areas in health informatics?
Emerging areas include health informatics risk management, decision analytics, informatics nursing, and health data science.
6. What are the challenges in health informatics?
Challenges include data interoperability, data privacy and security, lack of qualified professionals, resistance to change, and ethical considerations.
7. What are the benefits of health informatics?
Benefits include improved patient outcomes, enhanced efficiency and productivity, reduced costs, increased patient satisfaction, and advanced medical research.
8. What is the future of health informatics?
Health informatics is a rapidly evolving field, driven by advancements in technology and the growing need for data-driven healthcare solutions. Health informatics professionals will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of healthcare.