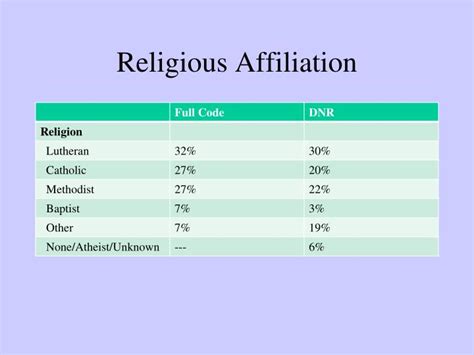
What is Religion Affiliation?
Religion affiliation refers to an individual’s identification with a particular religion or belief system. It encompasses a range of factors, including:

- Beliefs: Adherence to a set of religious doctrines and tenets
- Practices: Participation in religious rituals, ceremonies, and observances
- Community: Membership in a religious group or organization
- Identity: Self-identification as a follower of a specific religion
Types of Religion Affiliation
Religion affiliation can be categorized in various ways, including:
Denominational Affiliation
Individuals may affiliate with specific denominations within a larger religion, such as different denominations of Christianity (e.g., Catholic, Protestant, Orthodox).
Non-Denominational Affiliation
Some individuals may identify with a religion without belonging to a specific denomination, adhering only to the core beliefs and practices of that religion.
Secular Affiliation
Individuals may also choose to identify as secular, meaning they do not affiliate with any particular religion or belief system.
Conversion
Religion affiliation can change over time through conversion, where individuals adopt a new religion or abandon their previous one.
Importance of Religion Affiliation
Religion affiliation plays a significant role in many aspects of life:
- Social Cohesion: Religious communities provide a sense of belonging and support, fostering social cohesion and well-being.
- Cultural Identity: Religion often shapes cultural values, traditions, and norms, influencing individual identities.
- Moral Compass: Religious teachings offer moral guidance and ethical principles, shaping individuals’ values and behaviors.
- Mental and Physical Health: Studies have linked religion affiliation with improved mental and physical health outcomes.
Statistics on Religion Affiliation
According to the Pew Research Center’s 2021 Global Religious Landscape Study:
- 83% of the world’s population identifies with a religion, while 17% are unaffiliated.
- Christianity is the largest religion, with 31% of the world’s population, followed by Islam (24%), Hinduism (15%), Buddhism (7%), and Judaism (0.2%).
- Religious affiliation varies significantly by region, with high levels in the Middle East, North Africa, and South Asia, and lower levels in Europe and East Asia.
Measuring Religion Affiliation
Religion affiliation can be measured through surveys, censuses, and other data collection methods. Common indicators include:
- Self-Identification: Individuals are asked to indicate their religious affiliation.
- Religious Observance: Participation in religious practices or attendance at religious services.
- Religious Upbringing: The religion in which individuals were raised.
Tips for Understanding Religion Affiliation
- Respect Diversity: Be aware of the diversity of religious beliefs and practices.
- Avoid Assumptions: Do not assume that someone’s religion affiliation based on their appearance or background.
- Ask Open-Ended Questions: Engage in respectful conversations to learn more about individuals’ religious beliefs.
- Consider Context: Understand the cultural and historical context that shapes religion affiliation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overgeneralizing: Do not assume that all members of a particular religion are alike.
- Stereotyping: Avoid creating stereotypical assumptions about individuals based on their religion affiliation.
- Disrespecting Beliefs: Be respectful of others’ religious beliefs, even if they differ from your own.
FAQs on Religion Affiliation
1. What is the most common religion in the world?
Christianity is the largest religion, with 31% of the world’s population.
2. What factors influence religion affiliation?
Religion affiliation is shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including culture, family background, personal experiences, and social interactions.
3. Can religion affiliation change over time?
Yes, religion affiliation can change through conversion or other factors that lead individuals to adopt or abandon a particular religion.
4. What are the benefits of religion affiliation?
Religion affiliation can provide social cohesion, cultural identity, moral guidance, and improved mental and physical health outcomes.
5. How is religion affiliation measured?
Religion affiliation is typically measured through surveys, censuses, and other data collection methods, which may include self-identification, religious observance, and religious upbringing.
6. Is it important to respect religious diversity?
Yes, it is crucial to respect the diversity of religious beliefs and practices to promote a harmonious and inclusive society.
7. What should I do if I am unsure about someone’s religion affiliation?
If you are unsure about someone’s religion affiliation, avoid making assumptions and engage in respectful conversations to learn more about their beliefs.
8. What are some common stereotypes associated with religion affiliation?
Common stereotypes associated with religion affiliation include assuming that all members of a particular religion are alike, believing that all religious individuals are dogmatic, or disregarding the importance of religion in individuals’ lives.