Oxford’s Climate: A Statistical Snapshot
In the heart of Ohio, nestled amidst rolling hills and lush greenery, lies the quaint town of Oxford. Its picturesque streets and charming architecture belie a fascinating climate story, one that paints a vibrant tapestry of seasonal extremes and weather patterns.

According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Oxford enjoys a humid continental climate characterized by hot, humid summers and cold, snowy winters. The town’s proximity to the Great Lakes and its location in the humid continental climate zone significantly influence its temperature patterns.
Temperature Trends and Extremes
Over the past century, Oxford has experienced a gradual increase in average temperatures, mirroring a global trend attributed to climate change. NOAA data reveals that the town’s average annual temperature has risen by approximately 2 degrees Fahrenheit since the early 1900s.
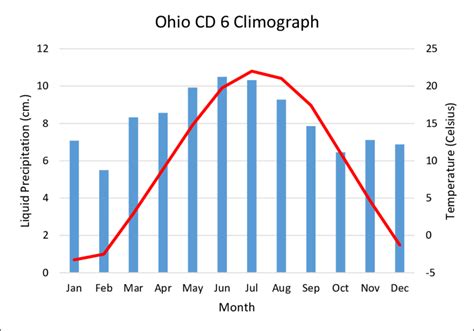
Yearly temperature fluctuations are evident in the town’s seasonal variations. Summer months, typically spanning from June to August, boast average temperatures ranging from 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 29 degrees Celsius), with occasional spikes into the 90s (32+ degrees Celsius). In contrast, winter months, extending from December to February, bring frigid conditions, with average temperatures plummeting to 20-30 degrees Fahrenheit (-6 to -1 degrees Celsius). Extreme cold spells can occasionally drive temperatures below zero.
Oxford’s Thermal Extremes
Oxford’s temperature history is marked by notable extremes, both in terms of heat and cold. The town’s highest recorded temperature stands at 106 degrees Fahrenheit (41 degrees Celsius), observed in July 1936. Conversely, its lowest recorded temperature, a bone-chilling -26 degrees Fahrenheit (-32 degrees Celsius), occurred in January 1994.
Seasonal Temperature Patterns
Oxford’s temperature patterns exhibit distinct seasonal variations, each with its own unique characteristics:
Spring: A Season of Transition (March-May)
Spring ushers in a welcome respite from the harshness of winter. Average temperatures rise steadily, ranging from 40 to 60 degrees Fahrenheit (4 to 16 degrees Celsius). As days lengthen and nature awakens from its slumber, Oxford’s landscapes transform into vibrant hues of green.
Summer: Heat and Humidity Intensify (June-August)
Summer brings Oxford’s most sweltering months, with average temperatures hovering around 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 29 degrees Celsius). High humidity levels can amplify the heat, making outdoor activities less comfortable. Thunderstorms and heavy downpours are not uncommon during this season.
Fall: A Colorful Farewell to Warmth (September-November)
Fall paints Oxford in a vibrant tapestry of crimson, gold, and orange. As days shorten and temperatures gradually decline, the town experiences average temperatures between 50 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit (10 to 21 degrees Celsius). Crisp autumn air and sunny days create ideal conditions for outdoor exploration.
Winter: Cold and Snowy Embrace (December-February)
Winter transforms Oxford into a winter wonderland. Average temperatures drop sharply, ranging from 20 to 30 degrees Fahrenheit (-6 to -1 degrees Celsius). Snowfall is frequent during this season, with an average annual accumulation exceeding 30 inches (76 centimeters). Icy conditions and strong winds can create hazardous driving conditions.
Oxford’s Climate in Context
Oxford’s climate fits within the broader context of Ohio’s humid continental climate. The state experiences similar seasonal temperature patterns, with hot, humid summers and cold, snowy winters. However, Oxford’s proximity to the Great Lakes moderates its climate somewhat, resulting in slightly milder temperatures compared to inland areas of Ohio.
The Impact of Climate Change on Oxford’s Temperature
Like many regions around the globe, Oxford is not immune to the effects of climate change. Rising global temperatures are impacting the town’s climate patterns in several ways:
Rising Temperatures
Average temperatures in Oxford have been on a gradual upward trend in recent decades. This warming trend is expected to continue in the future, leading to hotter summers and milder winters.
More Extreme Weather Events
Climate change is also contributing to an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as heat waves, droughts, and heavy rainfall. Oxford has experienced several such events in recent years, including record-breaking heatwaves and torrential downpours.
Strategies for Adapting to a Changing Climate
In light of the challenges posed by climate change, Oxford and its residents are taking proactive steps to adapt to a changing climate:
Infrastructure Upgrades
The town is investing in infrastructure upgrades to mitigate the effects of extreme weather events. These upgrades include improvements to stormwater management systems, floodwalls, and emergency response plans.
Community Engagement
Oxford is actively engaging its community in climate change adaptation efforts. The town hosts workshops, public forums, and educational campaigns to raise awareness and encourage individual action.
Green Initiatives
Oxford has set ambitious goals for reducing its carbon footprint and promoting sustainability. These initiatives include transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, and planting trees.
Conclusion
Oxford, Ohio, offers a fascinating case study of temperature patterns and climate change impacts. The town’s humid continental climate, with its hot summers and cold winters, provides a backdrop for understanding the effects of rising global temperatures. As Oxford navigates the challenges of climate change, its proactive approach to adaptation serves as a model for communities across the country. By embracing innovative strategies and fostering community collaboration, Oxford is building a more resilient and sustainable future for its residents and generations to come.