Are you preparing for the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT)? Understanding the MCAT score conversion process is crucial for interpreting your performance and gauging your chances of admission to medical school. This comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need to convert your raw scores into scaled scores and percentile ranks.

Understanding the MCAT Score Conversion
The MCAT is a standardized exam consisting of four sections: Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems, Chemical and Physical Foundations of Biological Systems, Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior, and Critical Analysis and Reasoning Skills. Each section is scored on a scale of 118-132.
Your raw scores are converted into scaled scores using a statistical process called equating. Equating ensures that scores from different test administrations are comparable, even if the difficulty of the exams varies. The scaled scores for each section are then combined to create a Composite Score, which ranges from 472 to 528.
MCAT Score Conversion Table
The following table shows the conversion between raw scores and scaled scores for each MCAT section:
| Raw Score | Scaled Score |
|---|---|
| 129-132 | 132 |
| 126-128 | 131 |
| 123-125 | 130 |
| 120-122 | 129 |
| 118-119 | 128 |
| … | … |
| 105-107 | 118 |
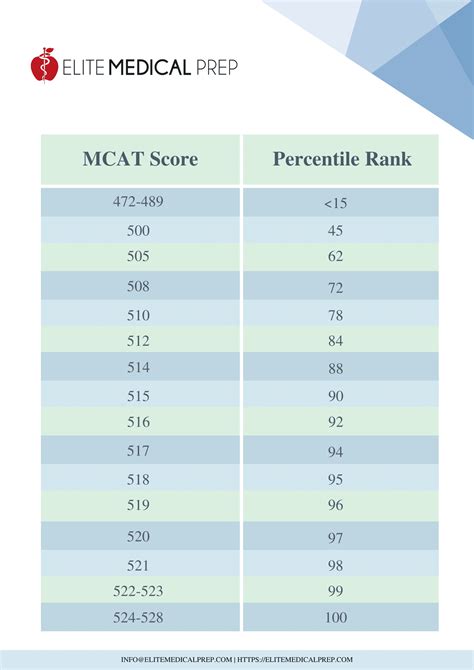
MCAT Percentile Rank Conversion Table
Your scaled score is also converted into a percentile rank, which indicates your performance relative to other test-takers. The following table shows the percentile ranks corresponding to different scaled scores:
| Scaled Score | Percentile Rank |
|---|---|
| 528 | 99th+ |
| 526 | 98th+ |
| 524 | 97th+ |
| … | … |
| 500 | 75th |
| 498 | 70th |
| 496 | 65th |
| … | … |
| 472 | 1st |
Significance of MCAT Scores
MCAT scores play a significant role in the medical school admissions process. The average MCAT score for successful applicants to U.S. medical schools is approximately 510. However, the competitiveness of medical schools varies, and some schools may require higher scores.
Medical School Admissions Cutoff Scores
While most medical schools do not have official cutoff scores, many schools use a screening process to filter out applicants with lower MCAT scores. The following table shows the MCAT Composite Score cut-off points for some top-ranked medical schools:
| Medical School | MCAT Composite Score Cut-off |
|---|---|
| Harvard Medical School | 518 |
| Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine | 517 |
| Stanford University School of Medicine | 517 |
| University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine | 517 |
| Yale School of Medicine | 517 |
Improving Your MCAT Score
If you are not satisfied with your MCAT score, there are several strategies you can implement to improve your performance:
- Study effectively: Use high-quality study materials, focus on understanding concepts rather than memorizing facts, and practice answering questions under time constraints.
- Take practice tests: Regular practice tests will help you identify areas of weakness and track your progress.
- Get feedback from experts: Seek guidance from a tutor or mentor who can provide personalized feedback and support.
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques and take breaks during your study sessions to reduce stress levels.
Conclusion
Understanding the MCAT score conversion process is essential for interpreting your performance and planning your medical school application. By understanding how your raw scores are converted into scaled scores and percentile ranks, you can assess your competitiveness for admission to your target schools. If you are not satisfied with your score, remember that there are strategies you can implement to improve your performance and increase your chances of success.