Overview

The Cold War, a period of intense political and military tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, marked a pivotal chapter in global history. From the post-World War II era to the late 20th century, this multifaceted conflict shaped nations, ideologies, and the international landscape. This DBQ (Document-Based Question) examines the complex factors that ignited the Cold War and its far-reaching consequences.
Causes of the Cold War
1. Ideological Divide
The fundamental ideological differences between the United States’ capitalist democracy and the Soviet Union’s communist dictatorship laid the groundwork for the Cold War. The US feared the spread of communism, while the USSR sought to establish its sphere of influence.
2. Post-War Tensions
The mistrust and suspicion that arose during World War II escalated after the conflict. The US and USSR emerged as global superpowers, each seeking to assert its dominance. The unresolved issue of post-war settlements and reparations fueled tensions.
3. Soviet Expansionism
The Soviet Union’s rapid expansion into Eastern Europe after the war raised concerns among Western powers. The establishment of communist regimes in Poland, Czechoslovakia, and other countries was seen as a threat to Western interests.
Consequences of the Cold War
1. Nuclear Arms Race
The Cold War fueled a relentless nuclear arms race as both sides sought to gain an advantage. By 1962, the US and USSR possessed over 50,000 nuclear warheads, raising the specter of global annihilation.
2. Proxy Wars
Direct military conflict between the superpowers was avoided, but they engaged in proxy wars around the globe. The Korean War (1950-1953), the Vietnam War (1955-1975), and the Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989) were all examples of this indirect confrontation.
3. Space Race
The Cold War also became a battleground for scientific and technological advancement. The launch of Sputnik by the USSR in 1957 sparked the “Space Race,” a competition to achieve dominance in space.
4. Cultural Divide
The Cold War permeated all aspects of society. It influenced art, literature, and popular culture, creating distinct cultural spheres between the East and the West.
Turning Points in the Cold War
1. Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
The Cuban Missile Crisis brought the world to the brink of nuclear war. The Soviet Union’s deployment of nuclear missiles in Cuba led to an intense standoff between the US and USSR, highlighting the fragility of peace during the Cold War.
2. Détente (1960s-1970s)
Periods of détente, or easing of tensions, occurred in the late 1960s and 1970s. The Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) sought to limit nuclear weapons, while the Helsinki Accords (1975) aimed to promote cooperation and human rights in Europe.
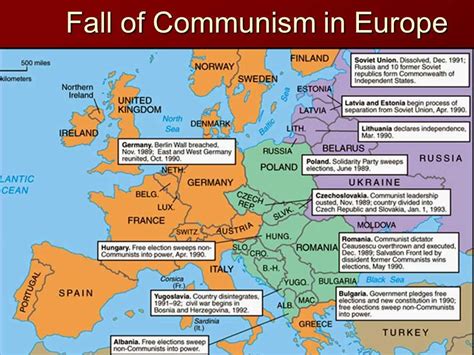
3. End of the Cold War (1989)
The collapse of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the end of the Cold War. The Soviet Union’s economic and political instability, coupled with the rise of Mikhail Gorbachev’s reformist policies, led to the disintegration of the Eastern Bloc and the eventual demise of the USSR.
Impact of the Cold War
1. Global Influence
The Cold War shaped the geopolitical landscape of the 20th century. It divided the world into two opposing spheres of influence, influencing the formation of alliances and international organizations.
2. Economic Consequences
The Cold War diverted substantial resources from civilian spending to military expenditures. The arms race and proxy wars had significant economic implications, particularly for the developing nations.
3. Legacy of Distrust
The Cold War left a legacy of distrust and suspicion between the US and Russia. The unresolved issues of nuclear proliferation and geopolitical rivalry continue to cast a shadow over international relations.
Tables
Table 1: Nuclear Warhead Count
| Year | US Warheads | USSR Warheads |
|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 150 | 0 |
| 1955 | 1,850 | 300 |
| 1962 | 6,000 | 3,000 |
| 1972 | 10,600 | 5,000 |
Table 2: Proxy Wars
| Conflict | Location | Years |
|---|---|---|
| Korean War | Korea | 1950-1953 |
| Vietnam War | Vietnam | 1955-1975 |
| Soviet-Afghan War | Afghanistan | 1979-1989 |
Table 3: Space Race Milestones
| Event | Date |
|---|---|
| Sputnik 1 launch | October 4, 1957 |
| Yuri Gagarin becomes first human in space | April 12, 1961 |
| Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin walk on the moon | July 20, 1969 |
| International Space Station launched | November 20, 1998 |
Table 4: Economic Impact of the Cold War
| Country | Military Expenditure as % of GDP |
|---|---|
| United States | 10-15% |
| Soviet Union | 12-18% |
| France | 5-8% |
| United Kingdom | 5-7% |
| Developing Countries | 2-5% |
Conclusion
The Cold War remains a complex and pivotal chapter in global history. Its intricate causes, far-reaching consequences, and lasting impact continue to influence international relations. By understanding the factors that ignited and shaped this conflict, we can gain invaluable insights into the challenges and opportunities of the modern era.