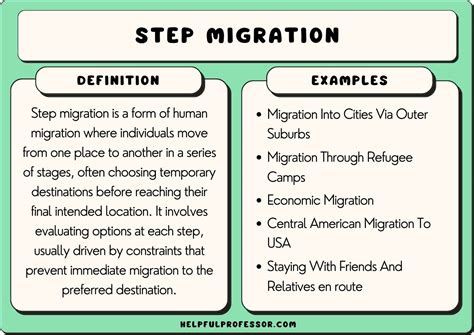
Step migration is a key concept in human geography that describes the process of gradual population movement from a place of origin to a final destination in stages. Understanding step migration is crucial for comprehending the patterns and dynamics of human mobility.

Stages of Step Migration
Step migration typically involves a series of intermediate stops between the origin and destination. These stops can be for various reasons, such as improved economic opportunities, better living conditions, or family reunification.
Push and Pull Factors
Push factors are conditions that motivate people to leave their home communities, such as economic hardship, political instability, or environmental disasters. Pull factors, on the other hand, are attractions that draw people to new destinations, such as job opportunities, better education, and higher living standards.
Types of Step Migration
There are two main types of step migration:
- Chain Migration: Involves a group of individuals or families from the same origin migrating to the same destination over time.
- Jump Migration: Occurs when individuals or families move over vast distances in a single step, often due to major economic or political disruptions.
Importance of Step Migration
Step migration has numerous implications for both the origin and destination communities:
- Origin Communities: Can experience population decline, brain drain, and social and economic disruption.
- Destination Communities: Can experience population growth, cultural diversity, and economic benefits.
Step Migration and Intervening Obstacles
Intervening obstacles, such as mountains, deserts, or cultural barriers, can influence the patterns of step migration. Individuals may have to make multiple stops or take longer routes to overcome these obstacles.
Historical Examples of Step Migration
Throughout history, numerous examples of step migration have occurred:
- European Migration to the United States: Many European immigrants moved from their homeland to intermediate destinations in Germany or the United Kingdom before finally settling in the US.
- Chinese Laborers in California: Chinese laborers moved from China to Hawaii and then to San Francisco in search of economic opportunities.
- Refugee Resettlement: Many refugees flee their home countries to neighboring countries or international resettlement agencies before eventually finding a permanent destination.
Applications of Step Migration
The concept of step migration can be applied to various fields, including:
- Urban Planning: Understanding step migration patterns can inform urban planning decisions related to housing, transportation, and infrastructure.
- Migration Policy: Policymakers can use step migration data to develop effective migration management strategies.
- Social Services: Step migration analysis helps identify vulnerable populations and provide targeted support services.
Tips for Migrating in Stages
For those considering migrating in stages, here are some tips to consider:
- Research Destination Communities: Gather information about potential destinations and compare factors such as job market, education, and living costs.
- Secure Financial Resources: Ensure you have sufficient funds to support yourself and your family throughout the migration process.
- Establish Connections: Connect with individuals or organizations in the destination community to ease your transition.
- Consider Legal Restrictions: Be aware of any legal restrictions on migration and obtain necessary documentation.
Tables
Table 1: Impact of Step Migration on Origin and Destination Communities
| Impact | Origin Communities | Destination Communities |
|---|---|---|
| Population Change | Decline | Growth |
| Demographic Changes | Ageing, brain drain | Cultural diversity |
| Economic Consequences | Reduced labor force, economic decline | Increased economic activity |
| Social Disruption | Loss of community cohesion | Social cohesion challenges |
Table 2: Push and Pull Factors of Step Migration
| Push Factors | Pull Factors |
|---|---|
| Economic hardship | Job opportunities |
| Political instability | Better education |
| Environmental disasters | Higher living standards |
| Social unrest | Family reunification |
Table 3: Types of Step Migration
| Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Chain Migration | Group movement from same origin to same destination |
| Jump Migration | Movement over vast distances in single step |
Table 4: Global Step Migration Patterns
| Region | Proportion of Migrants Engaged in Step Migration |
|---|---|
| Asia | 45% |
| Africa | 30% |
| Europe | 20% |
| North America | 15% |
| South America | 10% |
FAQs
-
Why do people engage in step migration?
– To overcome obstacles, access better opportunities, and reduce risks. -
What is the difference between chain migration and jump migration?
– Chain migration involves a group migration over time, while jump migration occurs in a single step. -
How does step migration affect origin communities?
– Can lead to population decline, brain drain, and social disruption. -
What are some tips for migrating in stages?
– Research destinations, secure financial resources, establish connections, and consider legal restrictions. -
What are the global patterns of step migration?
– Asia and Africa account for the majority of step migration globally. -
How can the concept of step migration be applied to other fields?
– In urban planning, migration policy, and social services.