Introduction
Propionic acid (CH3CH2COOH) is a simple organic acid with a wide range of industrial and consumer applications. Understanding its molecular structure, particularly its Lewis structure, is crucial for predicting its chemical behavior and designing new materials. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the CH3CH2COOH Lewis structure, exploring its key features, applications, and research directions.

CH3CH2COOH Lewis Structure
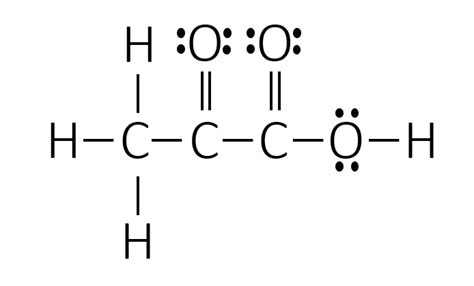
The Lewis structure of propionic acid can be drawn as follows:
O
||
CH3-CH2-C-OH
In this structure, the carbon atoms are represented by black circles, the hydrogen atoms by white circles, the oxygen atoms by red circles, and the covalent bonds by lines. The molecule has a central carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to a methyl group (CH3), a methylene group (CH2), and a hydroxyl group (OH).
Key Features
- Propionic acid is a polar molecule due to the electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen.
- The molecule adopts a tetrahedral geometry around the central carbon atom.
- The carboxylic acid group (COOH) is the functional group responsible for the acidic properties of propionic acid.
Physical Properties
- Molecular weight: 74.12 g/mol
- Melting point: -20.8 °C
- Boiling point: 141 °C
- Density: 0.993 g/mL
- Water solubility: Miscible
Chemical Properties
- Propionic acid is a weak acid with a pKa of 4.87.
- It undergoes typical carboxylic acid reactions, including esterification, amidation, and halogenation.
- Propionic acid can form hydrogen bonds, enabling it to participate in various intermolecular interactions.
Applications
Propionic acid finds numerous applications in various industries:
– Food and Beverage Industry: Preservative and flavoring agent in bread, cheese, and beverages.
– Pharmaceutical Industry: Ingredient in anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers.
– Textile Industry: Solvent for dyes and mordants.
– Agriculture: Herbicide and fungicide.
– Paper Industry: Sizing agent to improve paper strength.
Research Directions
Current research on propionic acid focuses on the following areas:
– Bio-based Production: Exploring sustainable methods for producing propionic acid from renewable feedstocks.
– Polymers and Composites: Developing new polymers and composites based on propionic acid derivatives for advanced materials.
– Drug Delivery Systems: Utilizing propionic acid as a drug carrier or targeting agent for improved drug delivery.
– Green Chemistry Applications: Identifying environmentally friendly uses of propionic acid in industrial processes.
Conclusion
The CH3CH2COOH Lewis structure provides a fundamental understanding of the molecular structure of propionic acid. This structure dictates its physical and chemical properties, making it a versatile substance with a wide range of applications. Ongoing research aims to further expand the utility of propionic acid in various fields, from pharmaceuticals to renewable energy sources. By harnessing the power of its molecular structure, propionic acid continues to play a significant role in modern science and industry.
Tables
Table 1: Physical Properties of Propionic Acid
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 74.12 g/mol |
| Melting point | -20.8 °C |
| Boiling point | 141 °C |
| Density | 0.993 g/mL |
| Water solubility | Miscible |
Table 2: Chemical Properties of Propionic Acid
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| pKa | 4.87 |
| Acid-base reactions | Esterification, amidation, halogenation |
| Intermolecular interactions | Hydrogen bonding |
Table 3: Applications of Propionic Acid
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Preservative, flavoring agent |
| Pharmaceutical | Anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers |
| Textile | Solvent for dyes, mordants |
| Agriculture | Herbicide, fungicide |
| Paper | Sizing agent |
Table 4: Research Directions for Propionic Acid
| Area | Focus |
|---|---|
| Bio-based Production | Sustainable production methods |
| Polymers and Composites | Advanced materials |
| Drug Delivery Systems | Improved drug delivery |
| Green Chemistry Applications | Environmentally friendly uses |
FAQs
Q1: What is the molecular weight of propionic acid?
A1: 74.12 g/mol
Q2: Is propionic acid a strong or weak acid?
A2: Weak acid with a pKa of 4.87.
Q3: What is the IUPAC name of propionic acid?
A3: Propanoic acid
Q4: Name two industrial applications of propionic acid.
A4: Preservative in food and solvent in the textile industry.
Q5: What is the hybridization of the central carbon atom in propionic acid?
A5: sp3
Q6: Can propionic acid form hydrogen bonds?
A6: Yes, due to the presence of the hydroxyl group.
Q7: What is a potential new application for propionic acid?
A7: As a bio-based feedstock for producing renewable fuels.
Q8: What are the latest advancements in propionic acid research?
A8: Development of bio-based production processes and functional materials based on propionic acid derivatives.