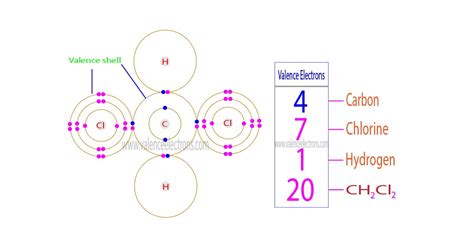
Overview of CH2Cl2 Valence Electrons
Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), also known as methylene chloride, is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH2Cl2. It is a colorless, volatile liquid with a sweet odor. CH2Cl2 is a polar molecule with a dipole moment of 1.62 D.

The carbon atom in CH2Cl2 has four valence electrons, and each chlorine atom has seven valence electrons. This gives CH2Cl2 a total of 26 valence electrons. The Lewis structure of CH2Cl2 is:
H:C:Cl
|
Cl
From the Lewis structure, we can see that the carbon atom is bonded to each chlorine atom with a single covalent bond. The remaining two valence electrons on the carbon atom are used to form two lone pairs.
Physical and Chemical Properties of CH2Cl2
CH2Cl2 is a versatile molecule with a wide range of physical and chemical properties. Some of the most important properties of CH2Cl2 are listed in the table below:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH2Cl2 |
| Molecular weight | 84.93 g/mol |
| Density | 1.326 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 40.1 °C |
| Melting point | -96.7 °C |
| Vapor pressure | 133 mmHg at 20 °C |
| Flash point | 12 °C |
| Flammability | Flammable |
| Toxicity | Harmful if inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin |
CH2Cl2 is a good solvent for a wide range of organic compounds. It is also used as a degreaser, a paint stripper, and a metal cleaner. CH2Cl2 is a moderate oxidizing agent and can react with some metals, such as aluminum and zinc.
Applications of CH2Cl2
CH2Cl2 is a versatile molecule with a wide range of applications. Some of the most important applications of CH2Cl2 are listed in the table below:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Solvent | CH2Cl2 is a good solvent for a wide range of organic compounds, including oils, greases, and waxes. |
| Degreaser | CH2Cl2 is used to remove grease and oil from metal surfaces. |
| Paint stripper | CH2Cl2 is used to remove paint from surfaces. |
| Metal cleaner | CH2Cl2 is used to remove rust and other contaminants from metal surfaces. |
| Oxidizing agent | CH2Cl2 is a moderate oxidizing agent and can be used to oxidize some metals. |
Safety Considerations
CH2Cl2 is a toxic substance and can cause a variety of health problems if inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin. The most common symptoms of CH2Cl2 exposure are:
- Eye irritation
- Skin irritation
- Respiratory irritation
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Confusion
- Unconsciousness
In severe cases, CH2Cl2 exposure can lead to death.
It is important to take precautions when working with CH2Cl2. These precautions include:
- Wearing protective clothing, including gloves, a respirator, and eye protection.
- Working in a well-ventilated area.
- Avoiding contact with the skin and eyes.
- Not ingesting CH2Cl2.
- Properly disposing of CH2Cl2 waste.
Conclusion
CH2Cl2 is a versatile molecule with a wide range of applications. However, it is important to be aware of the health risks associated with CH2Cl2 and to take appropriate precautions when working with it.
Introduction
Drug discovery is a complex and time-consuming process. One of the biggest challenges in drug discovery is identifying new lead compounds that have the potential to be developed into new drugs.
CH2Cl2 valence electrons could play a key role in drug discovery. By understanding the role of CH2Cl2 valence electrons in drug-target interactions, researchers could identify new lead compounds that are more likely to be effective and have fewer side effects.
CH2Cl2 Valence Electrons and Drug-Target Interactions
CH2Cl2 valence electrons can interact with drug targets in a number of ways. These interactions can include:
- Covalent bonding: CH2Cl2 valence electrons can form covalent bonds with drug targets. This type of interaction is typically strong and can lead to a high level of specificity.
- Ionic bonding: CH2Cl2 valence electrons can form ionic bonds with drug targets. This type of interaction is typically weaker than covalent bonding, but it can still be significant.
- Hydrogen bonding: CH2Cl2 valence electrons can form hydrogen bonds with drug targets. This type of interaction is typically weak, but it can still play a role in drug-target interactions.
- Van der Waals forces: CH2Cl2 valence electrons can interact with drug targets through van der Waals forces. This type of interaction is typically weak, but it can still contribute to the overall binding affinity between a drug and its target.
Applications of CH2Cl2 Valence Electrons in Drug Discovery
CH2Cl2 valence electrons could be used in a number of ways to improve drug discovery. These applications include:
- Identifying new lead compounds: CH2Cl2 valence electrons could be used to identify new lead compounds that have the potential to be developed into new drugs. By understanding the role of CH2Cl2 valence electrons in drug-target interactions, researchers could design new lead compounds that are more likely to be effective and have fewer side effects.
- Optimizing drug design: CH2Cl2 valence electrons could be used to optimize the design of new drugs. By understanding the role of CH2Cl2 valence electrons in drug-target interactions, researchers could design new drugs that are more potent, more selective, and have fewer side effects.
- Predicting drug efficacy: CH2Cl2 valence electrons could be used to predict the efficacy of new drugs. By understanding the role of CH2Cl2 valence electrons in drug-target interactions, researchers could predict which drugs are most likely to be effective in treating a particular disease.
Conclusion
CH2Cl2 valence electrons could play a key role in drug discovery. By understanding the role of CH2Cl2 valence electrons in drug-target interactions, researchers could identify new lead compounds, optimize drug design, and predict drug efficacy. This could lead to the development of new drugs that are more effective, have fewer side effects, and are more affordable.
Introduction
Materials science is the study of the properties and applications of materials. CH2Cl2 valence electrons could play a key role in materials science by enabling the development of new materials with unique properties.
CH2Cl2 Valence Electrons and Materials Properties
CH2Cl2 valence electrons can influence the properties of materials in a number of ways. These effects include:
- Electrical conductivity: CH2Cl2 valence electrons can contribute to the electrical conductivity of materials. This effect is typically small, but it can be significant in some materials.
- Thermal conductivity: CH2Cl2 valence electrons can contribute to the thermal conductivity of materials. This effect is typically small, but it can be significant in some materials.
- Magnetic properties: CH2Cl2 valence electrons can contribute to the magnetic properties of materials. This effect is typically small, but it can be significant in some materials.
- Optical properties: CH2Cl2 valence electrons can contribute to the optical properties of materials. This effect is typically small, but it can be significant in some materials.
Applications of CH2Cl2 Valence Electrons in Materials Science
CH2Cl2 valence electrons could be used in a number of ways to improve materials science. These applications include:
- Developing new materials: CH2Cl2 valence electrons could be used to develop new materials with unique properties. These materials could have a wide range of applications, including in electronics, optics, and energy storage.
- Improving the properties of existing materials: CH2Cl2 valence electrons could be used to improve the properties of existing materials. For example, CH2Cl2 valence electrons could be used to increase the strength, toughness, or corrosion resistance of materials