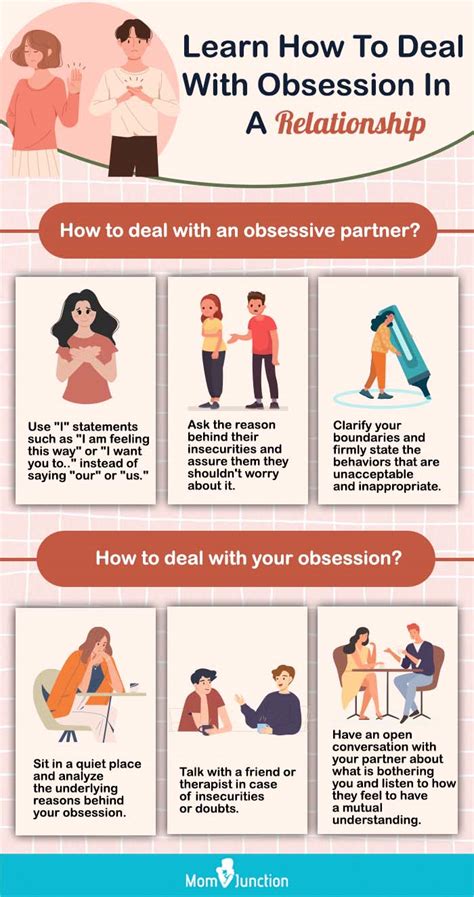
Personal reflection: Have you ever found yourself overly focused on a particular individual? The constant thoughts, the overwhelming desire to be around them, and the emotional rollercoaster that consumes you – these are telltale signs of an obsession. But what drives this intense preoccupation, and what can be done to regain control? In this article, we delve into the psychological underpinnings of obsession, exploring the motivations, pain points, and effective strategies for addressing this complex experience.

Definition: Obsession can be defined as a persistent, intrusive, and unwanted thought or idea that causes significant distress or impairs daily functioning. It can manifest in various forms, from intense attraction to compulsive behaviors or thoughts about a specific person.
Causes: The causes of obsession are complex and multifactorial, often involving a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. Some common contributing factors include:
- Neurochemical imbalances: Research suggests that imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, can contribute to obsessive thoughts and behaviors.
- Underlying mental health conditions: Obsession can be a symptom of anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), or other mental health conditions that involve excessive worry or rumination.
- Childhood experiences: Negative childhood experiences, such as trauma or abuse, can increase the risk of developing obsessions later in life.
- Personality traits: Certain personality traits, such as perfectionism, low self-esteem, and a need for control, can make individuals more susceptible to obsessions.
Pain Points: Obsession can be driven by a variety of emotional and psychological pain points, including:
- Insecurity and low self-esteem: Individuals with low self-esteem often seek validation and approval from others, which can lead to obsessive thoughts about a specific person who they perceive as having qualities they lack.
- Fear of abandonment: People who fear being left alone or rejected may develop obsessions as a way of coping with the anxiety associated with these fears.
- Unresolved emotional trauma: Unprocessed trauma or emotional pain from the past can surface in the form of obsessions, as the mind seeks to make sense of and resolve these experiences.
Overcoming obsession requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the underlying causes and the disruptive thoughts and behaviors associated with it. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Psychotherapy: Therapy can provide a safe and supportive environment to explore the underlying motivations behind obsession, develop coping mechanisms, and challenge maladaptive thought patterns. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure and response prevention (ERP), and psychodynamic therapy are common therapeutic approaches used to address obsessions.
2. Medication: In some cases, medication may be recommended to help manage the symptoms of obsession, particularly if they are severe or accompanied by anxiety or depression. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and other antidepressants can help regulate neurotransmitter imbalances and reduce intrusive thoughts.
3. Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga, can help calm the mind, reduce stress, and gain greater control over intrusive thoughts.
4. Self-care and support: Engaging in self-care activities, such as getting enough sleep, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet, can improve overall mental and emotional well-being, reducing the risk of developing obsessions. Building a strong support system of friends, family, or a support group can provide a sense of community and accountability.
- Identify and challenge triggers: Keep a journal to track the situations or people that tend to trigger obsessive thoughts. Once identified, develop strategies to avoid or manage these triggers effectively.
- Practice thought-stopping: When an obsessive thought arises, try to stop it in its tracks. Use a verbal cue, such as “Stop,” or focus on a physical sensation, such as squeezing your hand.
- Distract yourself: Engage in activities that you find enjoyable and distracting, such as reading, exercising, or spending time with loved ones.
- Refocus on reality: Remind yourself of the facts and evidence that contradict your obsessive thoughts. Challenge irrational beliefs and focus on more positive and realistic perspectives.
- Seek professional help: If your obsessive thoughts are causing significant distress or interfering with your daily life, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. A therapist can guide you through the process of overcoming obsession and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
Obsession is a complex and often distressing experience that can have significant consequences on our lives. Understanding the underlying causes, pain points, and effective strategies for addressing obsession is crucial for regaining control over our thoughts and emotions. By implementing the tips and strategies outlined in this article, we can learn to manage obsessive thoughts, break free from unhealthy patterns, and build healthier, more fulfilling relationships. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there is hope for recovery.