Introduction

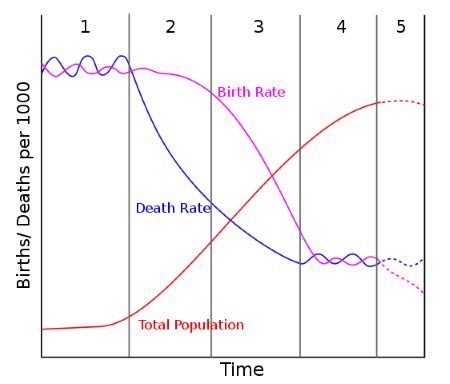
The natural increase rate (NIR) is a fundamental demographic measure that quantifies the rate at which a population grows or declines through natural means, namely the difference between birth rates and death rates. understanding NIR is critical for policymakers, public health professionals, and anyone interested in comprehending population dynamics and their implications for sustainable development.
Calculating NIR
NIR is calculated as follows:
NIR = Crude birth rate – Crude death rate
The crude birth rate measures the number of live births per 1,000 people in a population in a given year. The crude death rate, on the other hand, measures the number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population in a given year.
Significance of NIR
NIR provides insights into:
- Population growth: A positive NIR indicates a growing population, while a negative NIR indicates a declining population.
- Demographic stability: A stable NIR suggests that a population is maintaining its size, while significant fluctuations can indicate population imbalances.
- Health and well-being: A declining NIR can be a sign of declining health conditions or increased mortality rates, while a rising NIR can indicate improved healthcare and reduced mortality.
Influencing Factors
NIR is influenced by a multitude of factors, including:
- Healthcare: Access to quality healthcare, including maternal and child health services, can improve fertility rates and reduce mortality rates, leading to a higher NIR.
- Education: Educated individuals are more likely to make informed decisions about family planning, healthcare, and nutrition, which can positively impact NIR.
- Economic conditions: Economic stability and prosperity tend to correlate with lower mortality rates and higher birth rates, resulting in a higher NIR.
- Cultural norms: Social and cultural factors, such as attitudes towards childbearing and family size, can significantly impact NIR.
Current Trends
According to the World Bank, the global NIR has been declining steadily in recent decades. In 2022, the global NIR stood at 0.84%, down from 1.1% in 2000. This decline is primarily attributed to declining fertility rates, which have fallen below the replacement level in many developed countries.
Implications for Policymakers
The declining NIR presents policymakers with significant challenges and opportunities:
- Demographic challenges: A low NIR can lead to population aging, a shrinking workforce, and reduced economic productivity.
- Social implications: A declining population can impact the provision of essential services, such as healthcare and education.
- Sustainable development goals: NIR is a key indicator of a population’s ability to meet its sustainable development goals, such as improving health, education, and economic well-being.
Initiatives to Improve NIR
To address these challenges, policymakers can consider initiatives that:
- Promote family planning and reproductive health: Ensure access to contraception, counseling, and other services that empower individuals to make informed choices about childbearing.
- Invest in healthcare: Strengthen healthcare systems to reduce mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable populations.
- Promote economic growth and stability: Create conditions that lead to increased economic prosperity and stability, which can positively impact NIR.
- Address cultural norms: Sensitize communities and address cultural barriers that may hinder healthy reproductive practices.
Conclusion
The natural increase rate is a vital measure of population dynamics. Understanding NIR is crucial for policymakers, public health professionals, and anyone interested in sustainable development. While the global NIR has been declining, policymakers can implement measures to address the challenges and exploit the opportunities presented by this demographic trend.
Tables
- Table 1: Global NIR Trends
| Year | NIR (%) |
|—|—|—|
| 2000 | 1.1 |
| 2010 | 1.0 |
| 2020 | 0.9 |
| 2022 | 0.84 |
- Table 2: Factors Influencing NIR
| Factor | Impact |
|—|—|—|
| Healthcare | Positive |
| Education | Positive |
| Economic conditions | Positive |
| Cultural norms | Variable |
- Table 3: Initiatives to Improve NIR
| Initiative | Impact |
|—|—|—|
| Family planning | Positive |
| Healthcare investment | Positive |
| Economic growth | Positive |
| Cultural sensitivity | Positive |
- Table 4: Implications of a Declining NIR
| Implication | Impact |
|—|—|—|
| Population aging | Negative |
| Shrinking workforce | Negative |
| Reduced economic productivity | Negative |
| Increased dependency ratio | Negative |