Introduction
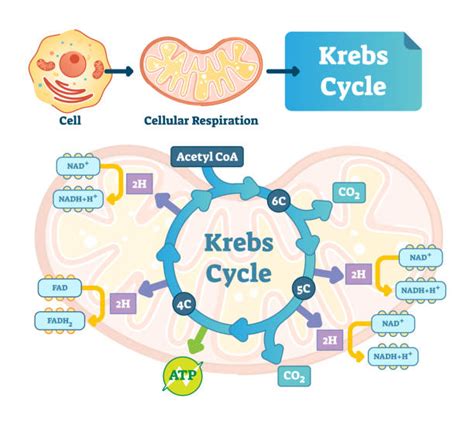
Pre-Krebs, also known as the citric acid cycle or the Krebs cycle, is a vital metabolic pathway that plays a crucial role in cellular respiration and the generation of energy. Understanding its function is essential for comprehending the fundamental processes that sustain life.

Primary Functions of Pre-Krebs
The primary functions of pre-Krebs can be summarized as follows:
1. Energy Production:
Pre-Krebs is primarily responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cellular energy currency. Through a series of chemical reactions, glucose and other nutrients are broken down, releasing energy that is captured and transferred to ATP molecules.
2. Anaplerosis and Cataplerosis:
Pre-Krebs serves as a central hub for intermediary metabolism. It replenishes (anaplerosis) and removes (cataplerosis) various metabolites, ensuring a continuous flow of precursors and building blocks for other metabolic reactions.
3. Redox Balance:
The cycle participates in redox reactions, transferring electrons and reducing equivalents to carriers such as NADH and FADH2. These carriers then transfer electrons to the electron transport chain, contributing to ATP production.
4. Precursor Synthesis:
Pre-Krebs provides precursors for the synthesis of essential molecules, including amino acids, nucleotides, and heme. These molecules play crucial roles in cell growth, DNA replication, and various metabolic processes.
Importance of Pre-Krebs
The importance of pre-Krebs is evident in its widespread presence across diverse organisms. It is essential for:
1. Cellular Respiration:
Pre-Krebs is the main pathway for the aerobic breakdown of glucose, providing energy for most cells in eukaryotic organisms.
2. Mitochondrial Function:
The cycle occurs within the mitochondria, the cellular powerhouses, and is intimately linked to mitochondrial function and bioenergetics.
3. Metabolic Homeostasis:
Pre-Krebs interacts with other metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation, to maintain metabolic balance and respond to changing cellular needs.
4. Health and Disease:
Dysregulation of pre-Krebs has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndromes.
Benefits of Pre-Krebs Function
The proper functioning of pre-Krebs brings numerous benefits, including:
1. Efficient Energy Production:
Pre-Krebs optimizes energy production by efficiently extracting and transferring energy from nutrients.
2. Metabolic Flexibility:
The cycle’s ability to respond to nutrient availability and cellular demand ensures metabolic flexibility and adaptability.
3. Precursor Supply:
Pre-Krebs provides a steady supply of precursors for various essential molecules, supporting cell growth and function.
4. Redox Regulation:
The cycle contributes to redox balance, preventing oxidative stress and maintaining cellular health.
Applications in Medicine and Research
Understanding pre-Krebs function has led to significant advances in medicine and research, including:
1. Diagnosis and Treatment:
Pre-Krebs metabolites and enzymes are used as biomarkers for diagnosing metabolic disorders and monitoring treatment efficacy.
2. Drug Development:
Inhibitors of pre-Krebs enzymes are being developed as potential drugs for treating cancer and other diseases.
3. Metabolic Engineering:
Researchers are manipulating pre-Krebs to engineer microorganisms and plants with improved production of biofuels and other valuable compounds.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between the citric acid cycle and the Krebs cycle?
The two terms refer to the same metabolic pathway. The citric acid cycle is the more common name, while the Krebs cycle is named after its discoverer, Hans Krebs.
2. Why is pre-Krebs important for life?
Pre-Krebs is essential for cellular respiration, which provides energy for all living organisms. It also plays a vital role in metabolism and the synthesis of essential molecules.
3. Can pre-Krebs function be impaired?
Yes, various genetic and acquired factors can impair pre-Krebs function, leading to metabolic disorders and diseases.
4. How is pre-Krebs studied in research?
Researchers use isotopic labeling, metabolomics, and genetic approaches to study pre-Krebs metabolism and its role in health and disease.
5. What are some potential applications of pre-Krebs research?
Applications include new treatments for metabolic diseases, metabolic engineering for sustainable bioproduction, and understanding the metabolic basis of aging.
6. How does pre-Krebs contribute to carbon dioxide production?
Pre-Krebs releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct of its reactions, which is then exhaled as a waste product of cellular respiration.
7. What is the significance of the pre-Krebs enzymes?
The enzymes of pre-Krebs are highly regulated and play critical roles in maintaining metabolic balance and responding to cellular signals.
8. Can pre-Krebs function be stimulated?
Certain dietary interventions, such as calorie restriction, can stimulate pre-Krebs function and promote mitochondrial health.
Conclusion
Pre-Krebs is a fundamental metabolic pathway that plays a critical role in cellular respiration, energy production, metabolite synthesis, and redox balance. Its importance extends to various aspects of health, disease, and metabolic engineering. Understanding its function is essential for comprehending the intricacies of cellular life and developing strategies to prevent and treat metabolic disorders.